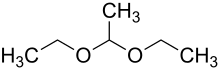
1,1-Diethoxyethane
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,1-Diethoxyethane | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.010 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H14O2 | |
| Molar mass | 118.176 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.83 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | −100 °C (−148 °F; 173 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 102 °C (216 °F; 375 K)[1] |
| 46 g/L[1] | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.3834 (20 °C)[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
1,1-Diethoxyethane (acetaldehyde diethyl acetal) is a major flavoring component of distilled beverages, especially malt whisky[3] and sherry.[4] Although it is just one of many compounds containing an acetal functional group, this specific chemical is sometimes called simply acetal.
References
- ^ a b c d "Data sheet of acetaldehyde" (PDF). Merck. Retrieved 2014-06-02.
- ^ Lide, David R., ed. (2009). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (90th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4200-9084-0.
- ^ Maarse, H. (1991). Volatile Compounds in Foods and Beverages. CRC Press. p. 553. ISBN 978-0-8247-8390-7.
- ^ Zea, Luis; Serratosa, María P.; Mérida, Julieta; Moyano, Lourdes (2015). "Acetaldehyde as Key Compound for the Authenticity of Sherry Wines: A Study Covering 5 Decades". Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety. 14 (6): 681–693. doi:10.1111/1541-4337.12159.
In sensory terms, 1,1-diethoxyethane and other acetals, acetoin, and sotolon are the main compounds formed from acetaldehyde in Sherry wines.