1816 United States presidential election in Connecticut
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elections in Connecticut |
|---|
 |
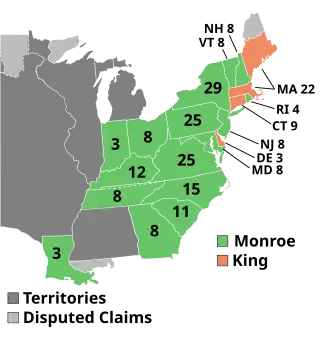
A presidential election was held in Connecticut on November 1, 1816 as part of the 1816 United States presidential election.[1] The senior U.S. senator from New York Rufus King, the de facto candidate of the Federalist Party, received nine votes from electors chosen by the Connecticut General Assembly.[2] Although commonly remembered as the last Federalist presidential candidate, King was not formally selected as the party's nominee and had no designated running mate; the Connecticut electors split their vice presidential votes between the former U.S. senator from Pennsylvania James Ross and the chief justice of the United States John Marshall.[3][4] This was the last election in which Connecticut's electoral votes were awarded by the state legislature.[5]
General election
Results
| Party | Candidate | Votes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federalist | Elijah Hubbard | ** | |
| Federalist | Jonathan Ingersoll | ** | |
| Federalist | Jirah Isham | ** | |
| Federalist | Samuel W. Johnson | ** | |
| Federalist | William Perkins | ** | |
| Federalist | Seth P. Staples | ** | |
| Federalist | Elisha Sterling | ** | |
| Federalist | Nathaniel Terry | ** | |
| Federalist | Asa Willey | ** | |
| Democratic-Republican | Oliver Wolcott Jr. | 88 | |
Total
|
>88
| ||
Electoral college
| For President | For Vice President | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Candidate | Party | Home state | Electoral vote |
Candidate | Party | Home state | Electoral vote |
| Rufus King | Federalist | New York | 9 | James Ross | Federalist | Pennsylvania | 5 |
| John Marshall | Federalist | Virginia | 4 | ||||
Total
|
9
|
Total
|
9
| ||||
See also
References
- ^ No candidate formally nominated. Connecticut electors cast 5 votes for James Ross and 4 votes for John Marshall.
- ^ Results of balloting in the Connecticut General Assembly. The number of votes cast for the successful Federalist candidates is unknown.
- ^ "The Legislature of this State [...]". Connecticut Courant. November 5, 1816.
- ^ a b Lampi, Philip J. "Connecticut 1816 Electoral College". A New Nation Votes. American Antiquarian Society. Retrieved March 10, 2025.
- ^ Turner, Lynn W. (2002). "Elections of 1816 and 1820". In Schlesinger, Arthur M. Jr.; Israel, Fred L. (eds.). History of American Presidential Elections, 1789–2001. Vol. 1. Philadelphia: Chelsea House Publishers. p. 307.
- ^ a b "1816 Electoral College Results". National Archives. Retrieved February 22, 2025.
- ^ Dubin, Michael J. (2002). United States Presidential Elections, 1788–1860: The Official Results by County and State. Jefferson, NC: McFarland & Co. p. xii.
_-_Google_Art_Project_(3x4_cropped).jpg)
.jpg)