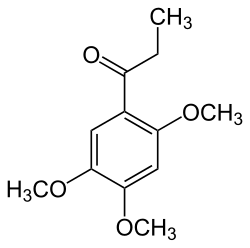
2,4,5-Trimethoxypropiophenone
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-(3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl)propan-1-one | |
| Other names
Isoacoramone
2,4,5-Trimethoxypropiophenone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 4-08-00-02746 | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H16O4 | |
| Molar mass | 224.256 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 109 °C (228 °F; 382 K) |
| Boiling point | 186 °C (367 °F; 459 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
2,4,5-Trimethoxypropiophenone is a natural phenylpropanoid and precursor in the synthesis of α-asarone.[1]
Natural occurrence
2,4,5-Trimethoxypropiophenone is a component of several plant species' essential oils. The chemical has been identified in Piper marginatum,[2] Acorus tatarinowii,[3] and Asarum maximum.[4]
References
- ^ Francisco, Díaz; Leticia, Contreras; Rosa, Flores; Joaquín, Tamariz; Fernando, Labarrios; Germán, Chamorro; Héber, Muñoz (1991). "An Efficient Synthesis of α-Asarone". Organic Preparations and Procedures International. 23 (2): 133–138. doi:10.1080/00304949109458299.
- ^ Oliveira Santos, Bárbara Viviana; Oliveira Chaves, Maria Célia (1999). "2,4,5-Trimethoxypropiophenone from Piper marginatum". Biochemical Systematics and Ecology. 27 (5): 539–541. Bibcode:1999BioSE..27..539O. doi:10.1016/S0305-1978(98)00109-4.
- ^ Jinfeng, Hu; Xiaozhang, Feng (2000). "Phenylpropanes from Acorus tatarinowii". Planta Medica. 66 (7): 662–664. doi:10.1055/s-2000-8628. PMID 11105577. S2CID 260283667.
- ^ X., Wang; Long, C.; Cai, S.; Zhao, Y. (2000). "Studies on the Chemical Constituents of the Root of Asarum maximum". Zhong Cao Yao. 31 (12): 888–890.