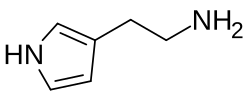
3-Pyrrolylethylamine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 3-NEA; 2-(1H-Pyrrol-3-yl)ethylamine; 3-(2-Aminoethyl)pyrrole |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C6H10N2 |
| Molar mass | 110.160 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
3-Pyrrolylethylamine (3-NEA or 2-(1H-pyrrol-3-yl)ethylamine) is a chemical compound of the arylalkylamine family.[1] It can be thought of as the analogue of tryptamine (2-indolylethylamine) in which the benzene component of the indole ring has been removed, leaving only a pyrrole ring.[1]
The compound is also related to other arylalkylamines as well as trace amines including phenethylamine (2-phenylethylamine), 2-furylethylamine, thiopropamine (1-(2-thienyl)-2-aminopropane), and isocyclamine (cyclopentanylaminopropane), among others.[1] Many of these compounds are monoamine releasing agents and/or reuptake inhibitors.[1]
3-NEA was first described in the scientific literature by 1965.[1]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e Shulgin A, Manning T, Daley PF (2011). "#67. FEA". The Shulgin Index, Volume One: Psychedelic Phenethylamines and Related Compounds. Vol. 1. Berkeley, CA: Transform Press. pp. 138–141. ISBN 978-0-9630096-3-0. OCLC 709667010.