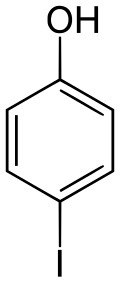
4-Iodophenol
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-Iodophenol
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.951 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H5IO | |
| Molar mass | 220.009 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.8573 g/cm3 (112 °C)[1] |
| Melting point | 93.5 °C (200.3 °F; 366.6 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 139 °C (282 °F; 412 K)[1] (5 mmHg; decomposes) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.33[2] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  [3] [3]
| |
| H302, H312, H314 | |
| P280, P305+P351+P338, P310 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
4-Iodophenol (p-iodophenol) is an aromatic organic compound. A colorless solid, it is one of three monoiodophenols. 4-Iodophenol undergoes a variety of coupling reactions in which the iodine substituent is replaced by a new carbon group para to the hydroxy group of the phenol.[3] It is also used to enhance chemiluminescence for detection of cancer cells[4] and in the Eclox assay.
4-Iodophenol can be prepared from 4-aminophenol via the diazonium salt. An alternative synthesis involves reaction of salicylic acid with iodine, followed by decarboxylation.[5]
References
- ^ a b c Haynes, p. 3.324
- ^ Haynes, p. 5.93
- ^ a b "4-Iodophenol". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ^ "4-Iodophenol". Fisher Scientific.
- ^ Dains, F. B.; Eberly, Floyd (1935). "p-Iodophenol". Organic Syntheses. 15: 39. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.015.0039.
Cited sources
- Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 9781498754293.