Acylphosphatase
| acylphosphatase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 3.6.1.7 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 9012-34-4 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Acylphosphatase | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
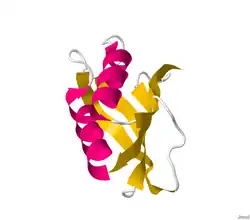
 Structure of acylphosphatase.[2] | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | Acylphosphatase | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF00708 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001792 | ||||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00136 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1aps / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
In enzymology, an acylphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.7) is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of the carboxyl-phosphate bond of acylphosphates, with acylphosphate and H2O as the two substrates of this enzyme, and carboxylate and phosphate as its two products:[3]
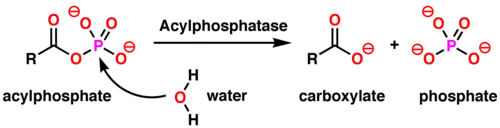
Function
This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, specifically those acting on acid anhydrides in phosphorus-containing anhydrides. The systematic name of this enzyme class is acylphosphate phosphohydrolase. Other names in common use include acetylphosphatase, 1,3-diphosphoglycerate phosphatase, acetic phosphatase, Ho 1-3, and GP 1-3.
This enzyme participates in 3 metabolic pathways:
- glycolysis / gluconeogenesis
- pyruvate metabolism, and
- benzoate degradation via coa ligation.
Structural studies
Structures of this enzyme have been solved by both NMR and X-ray crystallography. See the links to PDB structures in the info boxes on the right for a current list of structures available in the PDB. The protein contains a beta sheet stacked on two alpha helices described by CATH as an Alpha-Beta Plait fold. The active site sits between sheet and helices and contains an arginine and an asparagine.[4] Most structures are monomeric [5]
Isozymes
Humans express the following two acylphosphatase isozymes:
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- ^ "RCSB Protein Data Bank - Structure Summary for 2W4P - HUMAN COMMON-TYPE ACYLPHOSPHATASE VARIANT, A99G".
- ^ Pastore A, Saudek V, Ramponi G, Williams RJ (March 1992). "Three-dimensional structure of acylphosphatase. Refinement and structure analysis". J. Mol. Biol. 224 (2): 427–40. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(92)91005-A. PMID 1313885.
- ^ Stefani M, Taddei N, Ramponi G (February 1997). "Insights into acylphosphatase structure and catalytic mechanism". Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 53 (2): 141–51. doi:10.1007/PL00000585. PMC 11147357. PMID 9118002. S2CID 24072481.
- ^ Gribenko AV, Patel MM, Liu J, McCallum SA, Wang C, Makhatadze GI (February 2009). "Rational stabilization of enzymes by computational redesign of surface charge-charge interactions". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 106 (8): 2601–6. Bibcode:2009PNAS..106.2601G. doi:10.1073/pnas.0808220106. PMC 2650310. PMID 19196981.
- ^ "Enzyme 3.6.1.7". PDBe Enzyme Browser.