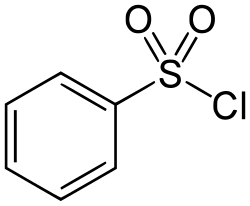
Benzenesulfonyl chloride
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Benzenesulfonyl chloride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.397 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H5ClO2S | |
| Molar mass | 176.62 |
| Appearance | colourless liquid |
| Density | 1.384 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| Melting point | 13 to 14 °C (55 to 57 °F; 286 to 287 K) |
| reacts | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Benzenesulfonyl chloride is an organosulfur compound with the formula C6H5SO2Cl. It is a colourless viscous oil that dissolves in organic solvents, but reacts with compounds containing reactive N-H and O-H bonds. It is mainly used to prepare sulfonamides and sulfonate esters by reactions with amines and alcohols, respectively.[1] The closely related compound toluenesulfonyl chloride is often preferred analogue because it is a solid at room temperature and easier to handle.
Production
The compound is prepared by the chlorosulfonation of benzene:
- C6H6 + 2SHO3SCl → C6H5SO2Cl + HCl + SO3
Benzenesulfonic acid is an intermediate in this conversion. Diphenylsulfone is a side product.
Benzenesulfonyl chloride can also be prepared by treating benzenesulfonate salts with phosphorus oxychloride.[2]
Reactions
Benzenesulfonyl chloride is an electrophilic reagent. It hydrolyzes with heat but is stable toward cold water.[2] Amines react to give sulfonamides. This reaction is the basis of the Hinsberg test for amines.[3]
References
- ^ Lindner, Otto; Rodefeld, Lars (2000). "Benzenesulfonic Acids and Their Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_507. ISBN 978-3-527-30385-4.
- ^ a b Roger Adams, C. S. Marvel, H. T. Clarke, G. S. Babcock, and T. F. Murray (1921). "Benzenesulfonyl Chloride". Organic Syntheses. 1: 21. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.001.0021.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Ralph L. Shriner, Christine K. F. Hermann, Terence C. Morrill, David Y. Curtin, Reynold C. Fuson "The Systematic Identification of Organic Compounds", 8th Edition, 2003, Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-21503-5