Beryllium sulfide
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.033.680 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| BeS | |
| Molar mass | 41.077 g/mol |
| Appearance | white crystalline |
| Density | 2.36 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1,800 °C (3,270 °F; 2,070 K) decomposes |
| Decomposes | |
| Band gap | 7.4 eV |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.741 |
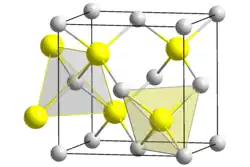
| Structure | |
| cubic | |
| F43m[1] | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
34 J/mol K |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
34 J/mol K |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−235 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 0.002 mg/m3 C 0.005 mg/m3 (30 minutes), with a maximum peak of 0.025 mg/m3 (as Be)[2] |
REL (Recommended)
|
Ca C 0.0005 mg/m3 (as Be)[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
Ca [4 mg/m3 (as Be)][2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Beryllium sulfide (BeS) is an ionic compound from the sulfide group with the formula BeS. It is a white solid with a sphalerite structure that is decomposed by water and acids.[3]
Preparation
Beryllium sulfide powders can be prepared by the reaction of sulfur and beryllium in a hydrogen atmosphere by heating the mixture for 10-20 minutes at temperatures from 1000-1300 °C. If done at 900 °C, there is beryllium metal impurities.[4]
Alternatively, it can be prepared by the reaction of beryllium chloride and hydrogen sulfide at 900 °C.[3][4]
References
- ^ Eugene Staritzky (1956). "Crystallographic Data. 121. Beryllium Sulfide, BeS". Analytical Chemistry. 28 (5): 915. doi:10.1021/ac60113a045.
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0054". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b Kenneth A. Walsh (2009). Beryllium Chemistry and Processing. ASM International. p. 127. ISBN 978-087170721-5.
- ^ a b William Zachariasen (1926). "Die Kristallstrunkturen von Berylliumoxyd und Berylliumsulfid" [The crystal structures of beryllium oxide and beryllium sulfide]. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie (in German). 119U (1): 201–213. doi:10.1515/zpch-1926-11921. S2CID 99383696.