Bhujel language
| Bhujel | |
|---|---|
| Bujhyal | |
| Region | Nepal (Tanahu District) Sikkim |
Native speakers | 22,000 (2011 census)[1] |
Sino-Tibetan
| |
| Devanagari Kharpa | |
| Official status | |
Official language in |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | byh |
| Glottolog | bujh1238 |
Bhujel, also called Bujhyal, is a Chepangic language of Greater Magaric Branch spoken in central Nepal and Sikkim in India. It is a semi-tonal language, employing a complex array of affixes. Bhujel are from Tibetan burman family. Bhujel people normally are with Mongoloid features rather than with Caucasoid features. Due to the social structure & social development, this term has been the identity of many other ethnic people too. Bhujel was granted additional official status in Sikkim in 2022.[2]
Geographical distribution
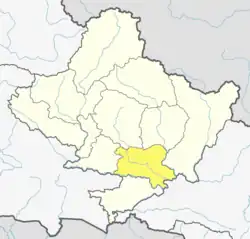
Bhujel is spoken in the following villages of Nepal (Ethnologue).
- Tanahun District, Gandaki Zone: Kulmun, Arthumpka, Andimul, and Baniyatar
- Gorkha District, Gandaki Zone: Beltar
- Nawalparasi District, Lumbini Zone: Dhodeni
- Chitwan District, Narayani Zone: Chanaute
Dialects
Ethnologue lists the following dialects of Bhujel.
- Kulmun
- Arthumpka
- Andimul
- Baniyatar
- Beltar
- Dhodeni
- Chanaute
References
- ^ Bhujel at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ "The Sikkim Official Languages Act" (PDF). sikkim.gov.in. Government of Sikkim. Retrieved 27 June 2025.