Carmantadine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | SCH-15427; NSC-172618 |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.048.869 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
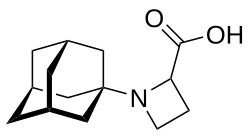
| Formula | C14H21NO2 |
| Molar mass | 235.327 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Carmantadine (INN, USAN; developmental code name SCH-15427) is an antiparkinsonian agent of the adamantane group that was never marketed.[1][2][3][4] It is structurally related to amantadine and shares some of its pharmacological actions.[2] Another related drug is dopamantine.[2][3][4] Carmantadine was first described by 1972 and is said to have reached early clinical trials.[1][2][3][4]
References
- ^ a b Elks J (2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer US. p. 13. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3. Retrieved 13 September 2024.
- ^ a b c d Vernier VG, du Pont E (1974). "Chapter 3. Antiparkinsonism Drugs". In Heinzelman RV (ed.). Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry. Vol. 9. Elsevier. pp. 19–26. doi:10.1016/s0065-7743(08)61424-4. ISBN 978-0-12-040509-1.
Carmantadine (VII, Sch 151427) is structurally related to amantadine33. It shares some of its pharmacological actions, was effective in a head—turning test34 and is in early clinical trials.
- ^ a b c Barnett A, Goldstein J, Taber R, Fiedler E (January 1974). "Pharmacology of Dopamantine and Carmantadine, 2 Potential Antiparkinson Agents". Pharmacologist. 16 (2): 205–.
- ^ a b c Goldstein J, Barnett A (January 1974). "Antagonism of electrically-induced heart-turning (HT) following intracaudate administration of dopamine (DA), amantadine (AM), apomorphine (APO), dopamantine and carmantadine". Pharmacologist. 16 (2): 206.