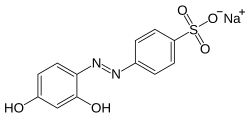
Chrysoine resorcinol
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sodium 4-[(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)diazenyl]benzenesulfonate
| |
| Other names
Sodium p-(2,4-dihydroxyphenylazo)benzenesulfonate; Chrysoine; Resorcinol Yellow; Gold Yellow; Yellow T; Tropaeolin O; Tropaeolin R; C.I. Food Yellow 8; C.I. Acid Orange 6; C.I. 14270
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.114 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H9N2NaO5S | |
| Molar mass | 316.26 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Orange-yellow solid |
| Partially soluble | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Chrysoine resorcinol is a synthetic azo dye which was formerly used as a food additive. In Europe, it was banned as a food additive in 1977.[1] In the US, it was banned in 1988.[2]
Chrysoine resorcinol can be used as a pH indicator with a color change between pH 11 and pH 12.7. In colorimetry, it has an absorption maximum of 387 nm.
| Chrysoine resorcinol (pH indicator) | ||
| below pH 11.0 | above pH 12.7 | |
| 11.0 | ⇌ | 12.7 |
Preparation
Acid orange 6 can be synthesised via the azo coupling of sulfanilic acid and resorcinol,
Notes
- ^ "EUR-Lex - Official Journal of the European Union".
- ^ "Chrysoine Resorcinol Properties, Molecular Formula, Applications - WorldOfChemicals". www.worldofchemicals.com. Retrieved 2022-07-12.
