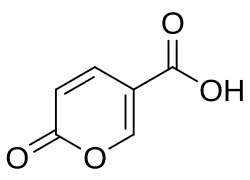
Coumalic acid
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Oxo-2H-pyran-5-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
Cumalic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.182 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H4O4 | |
| Molar mass | 140.094 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow solid |
| Melting point | 210 °C (410 °F; 483 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P264+P265, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P319, P321, P332+P317, P337+P317, P362+P364, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Coumalic acid is an organic compound with the molecular formula C6H4O4. Its melting point is around 210 °C.[1]
In laboratory coumalic acid may be obtained by self-condensation of malic acid in fuming sulfuric acid:[2]
References
- ^ Wiley, Richard H.; Knabeschuh, Louis H. (1955). "'2-Pyrones. XIII. The Chemistry of Coumalic Acid and its Derivatives". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 77: 1615. doi:10.1021/ja01611a062.
- ^ Richard H. Wiley and Newton R. Smith (1951). "Coumalic acid". Organic Syntheses. 31: 23. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.031.0023.