Cyheptamide
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Cyheptamine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.027.792 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
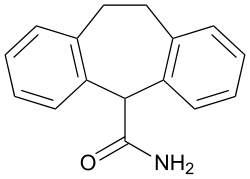
| Formula | C16H15NO |
| Molar mass | 237.302 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Cyheptamide was a investigational new drug that was developed by Ayerst Research Laboratories in the 1960s and was evaluated as an anticonvulsant.[1]
Cyheptamide undergoes significant metabolic transformation in both animals and humans, primarily through hydroxylation pathways.[2]
Cyheptamide exhibits moderate acute toxicity in animal models, with species-specific variations in lethal dose values.[3]
References
- ^ "Cyheptamide". Inxight: Drugs. NCATS. Retrieved 2025-06-25.
- ^ Kraml M, Sestanj K, Dvornik D (September 1971). "Metabolism of the anticonvulsant 10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo(a,d)cycloheptene-5-carboxamide. I. Metabolic fate of (14C)cyheptamide in animals and man". Biochemical Pharmacology. 20 (9): 2327–2338. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(71)90232-2. PMID 5163146.
- ^ van Eeken CJ, Birtwhistle RD, Mulder D (November 1970). "Toxicological study of cyheptamide: 10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cycloheptene-5-carboxamide (BS 7029)". Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Therapie. 188 (1): 79–85. PMID 5485105.