Diacetoxyscirpenol
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
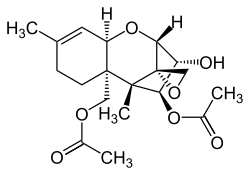
| IUPAC name
3α-Hydroxy-12α,13-epoxy-trichothec-9-ene-4β,15-diyl diacetate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,2′R,3R,4S,5S,5aR,9aR)-5a-[(Acetyloxy)methyl]-3-hydroxy-5,8-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,5a,6,7,9a-octahydrospiro[[2,5]methano[1]benzoxepine-10,2′-oxiran]-4-yl acetate | |
| Other names
anguidine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.159 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H26O7 | |
| Molar mass | 366.410 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Diacetoxyscirpenol (DAS), also called anguidine, is a mycotoxin from the group of type A trichothecenes. It is a secondary metabolite product of fungi of the genus Fusarium and may cause toxicosis in farm animals.[1] The US Health and Human Services agency considers it a select agent for research purposes.[2]
References
- ^ Hoerr FJ, Carlton WW, Yagen B (1981). "Mycotoxicosis caused by a single dose of T-2 toxin or diacetoxyscirpenol in broiler chickens". Vet. Pathol. 18 (5): 652–664. doi:10.1177/030098588101800510. PMID 7281462. S2CID 22715425.
- ^ "Select Agents and Toxins list". 17 May 2024.