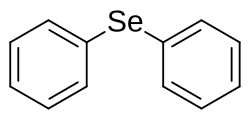
Diphenyl selenide
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H10Se | |
| Molar mass | 233.183 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow oil |
| Boiling point | 165–167 °C (329–333 °F; 438–440 K) 12 mm Hg |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H301, H331, H373, H410 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P301+P316, P304+P340, P316, P319, P321, P330, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Diphenyl selenide is an organoselenium compound with the formula (C6H5)2Se. A pale yellow viscous liquid, it is a member of the series diphenyl ether, diphenyl sulfide, and diphenyl telluride. It can be prepared by treating phenyldiazonium chloride with sodium polyselenide.[1]
Selected reactions
It can be oxidized with aqua regia to give diphenyl selenium dichloride.[2] When oxidized with hydrogen peroxide, diphenylselenoxide results.
References
- ^ Henry M. Leicester (1938). "Diphenyl Selenide". Organic Syntheses. 18: 27. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.018.0027.
- ^ Henry M. Leicester (1938). "Diphenylselenium Dichloride and Triphenylselenonium Chloride". Organic Syntheses. 18: 30. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.018.0030.