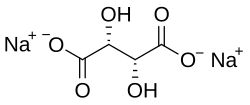
Sodium tartrate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
disodium (2R,3R)-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate
| |
| Other names
Sal tartar; Disodium tartrate; Bisodium tartrate; Sodium l-(+)-tartrate; E335
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H4Na2O6 (anhydrous) C4H8Na2O8 (dihydrate) | |
| Molar mass | 194.051 g/mol (anhydrous) 230.082 g/mol (dihydrate) |
| Appearance | white crystals |
| Density | 1.545 g/cm3 (dihydrate) |
| soluble | |
| Solubility | insoluble in ethanol |
| Pharmacology | |
| A06AD21 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Sodium tartrate (Na2C4H4O6) is a salt used as an emulsifier and a binding agent in food products such as jellies, margarine, and sausage casings. As a food additive, it is known by the E number E335.
It is made by the combination reaction of baking soda/Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) with tartaric acid.
Because its crystal structure captures a very precise amount of water, it is also a common primary standard for Karl Fischer titration, a common technique to assay water content.
