Equilin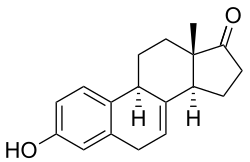 |
|
| Other names | Δ7-Estrone; 7-Dehydroestrone; Estra-1,3,5(10),7-tetraen-3-ol-17-one |
|---|
Routes of
administration | By mouth |
|---|
| Drug class | Estrogen |
|---|
|
(9S,13S,14S)-3-hydroxy-13-methyl-9,11,12,14,15,16-hexahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-one
|
| CAS Number | |
|---|
| PubChem CID | |
|---|
| DrugBank | |
|---|
| ChemSpider | |
|---|
| UNII | |
|---|
| KEGG | |
|---|
| ChEBI | |
|---|
| ChEMBL | |
|---|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
|---|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.809 |
|---|
|
| Formula | C18H20O2 |
|---|
| Molar mass | 268.356 g·mol−1 |
|---|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|---|
O=C3CC[C@H]4C/2=C/Cc1c(ccc(O)c1)[C@H]\2CC[C@]34C
|
InChI=1S/C18H20O2/c1-18-9-8-14-13-5-3-12(19)10-11(13)2-4-15(14)16(18)6-7-17(18)20/h3-5,10,14,16,19H,2,6-9H2,1H3/t14-,16+,18+/m1/s1 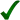 Y YKey:WKRLQDKEXYKHJB-HFTRVMKXSA-N  Y Y
|
| (verify) |
Equilin is a naturally occurring estrogen sex hormone found in horses as well as a medication.[1][2][3] It is one of the estrogens present in the estrogen combination drug preparations known as conjugated estrogens (CEEs; e.g. Premarin) and esterified estrogens (EEs; e.g. Estratab, Menest).[2][3] CEEs is the most commonly used form of estrogen medications in hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for menopausal symptoms in the United States.[3] Estrone sulfate is the major estrogen in CEEs (about 50%) while equilin sulfate is the second major estrogen in the formulation, present as about 25% of the total.[2][3]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Equilin is an estrogen, or an agonist of the estrogen receptors (ERs), the ERα and ERβ.[2] In terms of relative binding affinity for the ERs, equilin has about 13% and 49% of that of estradiol for the ERα and ERβ, respectively.[2] Analogously to the reversible transformation of estrone into estradiol by 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, equilin can be converted into the more potent estrogen 17β-dihydroequilin in the body.[2][3] This estrogen has about 113% and 108% of the relative binding affinities of estradiol for the ERα and ERβ, respectively.[2][3] Equilin is present in CEEs in the form of equilin sulfate, which itself is inactive and acts as a prodrug of equilin via steroid sulfatase.[2][3]
Similarly to synthetic estrogens like ethinylestradiol, equilin and CEEs have disproportionate effects in certain tissues such as the liver and uterus relative to bioidentical human estrogens like estradiol and estrone.[2] Because of their disproportionate potency in the liver, equilin and CEEs have relatively increased effects on liver protein synthesis compared to estradiol.[2]
A dosage of 0.25 mg/day equilin sulfate is equivalent to 0.625 mg/day CEEs in terms of relief from hot flashes.[2] At a dosage of 0.625 mg/day equilin sulfate, the increases in circulating levels of sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), corticosteroid-binding globulin, and angiotensinogen were 1.5 to 8 times those observed with estrone sulfate.[2] Equilin has about 42% of the relative potency of CEEs in the vagina and 80% of the relative potency of CEEs in the uterus, while its more active form, 17β-dihydroequilin, has about 83% of the relative potency of CEEs in the vagina and 200% of the relative potency of CEEs in the uterus.[2]
Relative oral potencies of estrogens
| Estrogen |
HFTooltip Hot flashes |
VETooltip Vaginal epithelium |
UCaTooltip Urinary calcium |
FSHTooltip Follicle-stimulating hormone |
LHTooltip Luteinizing hormone |
HDLTooltip High-density lipoprotein-CTooltip Cholesterol |
SHBGTooltip Sex hormone-binding globulin |
CBGTooltip Corticosteroid-binding globulin |
AGTTooltip Angiotensinogen |
Liver
|
| Estradiol |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0
|
| Estrone |
? |
? |
? |
0.3 |
0.3 |
? |
? |
? |
? |
?
|
| Estriol |
0.3 |
0.3 |
0.1 |
0.3 |
0.3 |
0.2 |
? |
? |
? |
0.67
|
| Estrone sulfate |
? |
0.9 |
0.9 |
0.8–0.9 |
0.9 |
0.5 |
0.9 |
0.5–0.7 |
1.4–1.5 |
0.56–1.7
|
| Conjugated estrogens |
1.2 |
1.5 |
2.0 |
1.1–1.3 |
1.0 |
1.5 |
3.0–3.2 |
1.3–1.5 |
5.0 |
1.3–4.5
|
| Equilin sulfate |
? |
? |
1.0 |
? |
? |
6.0 |
7.5 |
6.0 |
7.5 |
?
|
| Ethinylestradiol |
120 |
150 |
400 |
60–150 |
100 |
400 |
500–600 |
500–600 |
350 |
2.9–5.0
|
| Diethylstilbestrol |
? |
? |
? |
2.9–3.4 |
? |
? |
26–28 |
25–37 |
20 |
5.7–7.5
|
Sources and footnotes
Notes: Values are ratios, with estradiol as standard (i.e., 1.0). Abbreviations: HF = Clinical relief of hot flashes. VE = Increased proliferation of vaginal epithelium. UCa = Decrease in UCaTooltip urinary calcium. FSH = Suppression of FSHTooltip follicle-stimulating hormone levels. LH = Suppression of LHTooltip luteinizing hormone levels. HDL- C, SHBG, CBG, and AGT = Increase in the serum levels of these liver proteins. Liver = Ratio of liver estrogenic effects to general/systemic estrogenic effects (hot flashes/ gonadotropins). Sources: See template. |
Pharmacokinetics
Equilin has about 8% of the relative binding affinity of testosterone for SHBG, relative to 12% in the case of estrone.[2] In terms of plasma protein binding, it is bound 26% to SHBG and 13% to albumin.[2] The metabolic clearance rates of equilin and equilin sulfate are 2,640 L/day/m2 and 175 L/day/m2, respectively.[2] In accordance, the biological half-life of equilin sulfate is substantially longer than that of equilin.[2] Equilin is converted into 17β-dihydroequilin in the liver and in other tissues.[2][3] Equilin and 17β-dihydroequilin can also be transformed into equilenin and 17β-dihydroequilenin.[2][3] Equilin is excreted in the form of glucuronide conjugates.[2]
Chemistry
Equilin, also known as δ7-estrone or as 7-dehydroestrone, as well as estra-1,3,5(10),7-tetraen-3-ol-17-one, is a naturally occurring estrane steroid and an analogue of estrone.[2][3] In terms of chemical structure and pharmacology, equilin is to 17β-dihydroequilin (δ7-17β-estradiol) as estrone is to estradiol.[2][3]
References
|
|---|
| Estrogens | | ERTooltip Estrogen receptor agonists |
- Steroidal: Alfatradiol
- Certain androgens/anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone, testosterone esters, methyltestosterone, metandienone, nandrolone esters) (via estrogenic metabolites)
- Certain progestins (e.g., norethisterone, noretynodrel, etynodiol diacetate, tibolone)
- Clomestrone
- Cloxestradiol acetate
- Conjugated estriol
- Conjugated estrogens
- Epiestriol
- Epimestrol
- Esterified estrogens
- Estetrol†
- Estradiol
- Estradiol esters (e.g., estradiol acetate, estradiol benzoate, estradiol cypionate, estradiol enanthate, estradiol undecylate, estradiol valerate, polyestradiol phosphate, estradiol ester mixtures (Climacteron))
- Estramustine phosphate
- Estriol
- Estriol esters (e.g., estriol succinate, polyestriol phosphate)
- Estrogenic substances
- Estrone
- Estrone esters
- Ethinylestradiol#
- Hydroxyestrone diacetate
- Mestranol
- Methylestradiol
- Moxestrol
- Nilestriol
- Prasterone (dehydroepiandrosterone; DHEA)
- Promestriene
- Quinestradol
- Quinestrol
|
|---|
| Progonadotropins | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Antiestrogens | ERTooltip Estrogen receptor antagonists
(incl. SERMsTooltip selective estrogen receptor modulators/SERDsTooltip selective estrogen receptor downregulators) | |
|---|
| Aromatase inhibitors | |
|---|
| Antigonadotropins |
- Androgens/anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone, testosterone esters, nandrolone esters, oxandrolone, fluoxymesterone)
- D2 receptor antagonists (prolactin releasers) (e.g., domperidone, metoclopramide, risperidone, haloperidol, chlorpromazine, sulpiride)
- GnRH agonists (e.g., leuprorelin, goserelin)
- GnRH antagonists (e.g., cetrorelix, elagolix)
- Progestogens (e.g., chlormadinone acetate, cyproterone acetate, gestonorone caproate, hydroxyprogesterone caproate, medroxyprogesterone acetate, megestrol acetate)
|
|---|
| Others | |
|---|
|
|---|
- See also
- Estrogen receptor modulators
- Androgens and antiandrogens
- Progestogens and antiprogestogens
- List of estrogens
|
|
|---|
| ERTooltip Estrogen receptor | | Agonists |
- Steroidal: 2-Hydroxyestradiol
- 2-Hydroxyestrone
- 3-Methyl-19-methyleneandrosta-3,5-dien-17β-ol
- 3α-Androstanediol
- 3α,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel
- 3β,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel
- 3α-Hydroxytibolone
- 3β-Hydroxytibolone
- 3β-Androstanediol
- 4-Androstenediol
- 4-Androstenedione
- 4-Fluoroestradiol
- 4-Hydroxyestradiol
- 4-Hydroxyestrone
- 4-Methoxyestradiol
- 4-Methoxyestrone
- 5-Androstenediol
- 7-Oxo-DHEA
- 7α-Hydroxy-DHEA
- 7α-Methylestradiol
- 7β-Hydroxyepiandrosterone
- 8,9-Dehydroestradiol
- 8,9-Dehydroestrone
- 8β-VE2
- 10β,17β-Dihydroxyestra-1,4-dien-3-one (DHED)
- 11β-Chloromethylestradiol
- 11β-Methoxyestradiol
- 15α-Hydroxyestradiol
- 16-Ketoestradiol
- 16-Ketoestrone
- 16α-Fluoroestradiol
- 16α-Hydroxy-DHEA
- 16α-Hydroxyestrone
- 16α-Iodoestradiol
- 16α-LE2
- 16β-Hydroxyestrone
- 16β,17α-Epiestriol (16β-hydroxy-17α-estradiol)
- 17α-Estradiol (alfatradiol)
- 17α-Dihydroequilenin
- 17α-Dihydroequilin
- 17α-Epiestriol (16α-hydroxy-17α-estradiol)
- 17α-Ethynyl-3α-androstanediol
- 17α-Ethynyl-3β-androstanediol
- 17β-Dihydroequilenin
- 17β-Dihydroequilin
- 17β-Methyl-17α-dihydroequilenin
- Abiraterone
- Abiraterone acetate
- Alestramustine
- Almestrone
- Anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone and esters, methyltestosterone, metandienone (methandrostenolone), nandrolone and esters, many others; via estrogenic metabolites)
- Atrimustine
- Bolandiol
- Bolandiol dipropionate
- Butolame
- Clomestrone
- Cloxestradiol
- Conjugated estriol
- Conjugated estrogens
- Cyclodiol
- Cyclotriol
- DHEA
- DHEA-S
- ent-Estradiol
- Epiestriol (16β-epiestriol, 16β-hydroxy-17β-estradiol)
- Epimestrol
- Equilenin
- ERA-63 (ORG-37663)
- Esterified estrogens
- Estetrol
- Estradiol
- Estramustine
- Estramustine phosphate
- Estrapronicate
- Estrazinol
- Estriol
- Estrofurate
- Estrogenic substances
- Estromustine
- Estrone
- Etamestrol (eptamestrol)
- Ethinylandrostenediol
- Ethinylestradiol
- Ethinylestriol
- Ethylestradiol
- Etynodiol
- Etynodiol diacetate
- Hexolame
- Hippulin
- Hydroxyestrone diacetate
- Lynestrenol
- Lynestrenol phenylpropionate
- Mestranol
- Methylestradiol
- Moxestrol
- Mytatrienediol
- Nilestriol
- Norethisterone
- Noretynodrel
- Orestrate
- Pentolame
- Prodiame
- Prolame
- Promestriene
- RU-16117
- Quinestradol
- Quinestrol
- Tibolone
- Xenoestrogens: Anise-related (e.g., anethole, anol, dianethole, dianol, photoanethole)
- Chalconoids (e.g., isoliquiritigenin, phloretin, phlorizin (phloridzin), wedelolactone)
- Coumestans (e.g., coumestrol, psoralidin)
- Flavonoids (incl. 7,8-DHF, 8-prenylnaringenin, apigenin, baicalein, baicalin, biochanin A, calycosin, catechin, daidzein, daidzin, ECG, EGCG, epicatechin, equol, formononetin, glabrene, glabridin, genistein, genistin, glycitein, kaempferol, liquiritigenin, mirificin, myricetin, naringenin, penduletin, pinocembrin, prunetin, puerarin, quercetin, tectoridin, tectorigenin)
- Lavender oil
- Lignans (e.g., enterodiol, enterolactone, nyasol (cis-hinokiresinol))
- Metalloestrogens (e.g., cadmium)
- Pesticides (e.g., alternariol, dieldrin, endosulfan, fenarimol, HPTE, methiocarb, methoxychlor, triclocarban, triclosan)
- Phytosteroids (e.g., digitoxin (digitalis), diosgenin, guggulsterone)
- Phytosterols (e.g., β-sitosterol, campesterol, stigmasterol)
- Resorcylic acid lactones (e.g., zearalanone, α-zearalenol, β-zearalenol, zearalenone, zeranol (α-zearalanol), taleranol (teranol, β-zearalanol))
- Steroid-like (e.g., deoxymiroestrol, miroestrol)
- Stilbenoids (e.g., resveratrol, rhaponticin)
- Synthetic xenoestrogens (e.g., alkylphenols, bisphenols (e.g., BPA, BPF, BPS), DDT, parabens, PBBs, PHBA, phthalates, PCBs)
- Others (e.g., agnuside, rotundifuran)
|
|---|
Mixed
(SERMsTooltip Selective estrogen receptor modulators) | |
|---|
| Antagonists |
- Coregulator-binding modulators: ERX-11
|
|---|
|
|---|
| GPERTooltip G protein-coupled estrogen receptor | | Agonists | |
|---|
| Antagonists | |
|---|
| Unknown | |
|---|
|
|---|
- See also
- Receptor/signaling modulators
- Estrogens and antiestrogens
- Androgen receptor modulators
- Progesterone receptor modulators
- List of estrogens
|
