Ercanetide
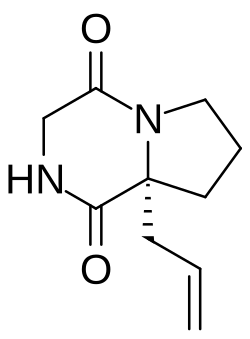 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Cyclo(L-glycyl-L-2-allylproline) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H14N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 194.234 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Ercanetide (INN;[1] developmental code name NNZ-2591) is a synthetic analog of cyclic glycine-proline (cGP) and experimental drug developed for Angelman syndrome, Phelan-McDermid syndrome, Pitt Hopkins syndrome,[2][3] and Prader-Willi syndrome.[4]
See also
- Traneurocin (NA-831)
References
- ^ https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/international-nonproprietary-names-(inn)/pl133.pdf
- ^ Markati, Theodora; Duis, Jessica; Servais, Laurent (3 July 2021). "Therapies in preclinical and clinical development for Angelman syndrome". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 30 (7): 709–720. doi:10.1080/13543784.2021.1939674. PMID 34112038.
- ^ Heussler, Helen S. (March 2021). "Emerging Therapies and challenges for individuals with Angelman syndrome". Current Opinion in Psychiatry. 34 (2): 123–128. doi:10.1097/YCO.0000000000000674. ISSN 0951-7367. PMID 33395098. S2CID 230663523.
- ^ "An Open-Label Study of Oral NNZ-2591 in Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS-001) (PWS-001) NCT05879614". clinicaltrials.gov. Retrieved 6 December 2023.