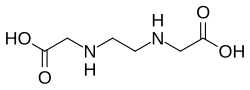
Ethylenediaminediacetic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2′-[Ethane-1,2-diylbis(azanediyl)]diacetic acid | |
| Other names
N,N′-Ethylenediglycine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.024.641 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H12N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 176.172 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 228 °C (442 °F; 501 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
| |
| Danger | |
| H302, H315, H318, H319, H335, H411 | |
| P261, P264, P264+P265, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+P317, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P305+P354+P338, P317, P319, P321, P330, P332+P317, P337+P317, P362+P364, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Ethylenediaminediacetic acid (EDDA) is the organic compound with the formula C2H4(NHCH2CO2H)2. It is a derivative of two molecules of glycine, wherein the amines are linked. It is a white solid. It is one of several aminopolycarboxylic acids.
The conjugate base is a tetradentate ligand.[1] A representative complex is Na[Co(EDDA)(CO3)].[2]
Related compounds
References
- ^ Sabo, Tibor J.; Grguric-Sipka, Sanja R.; Trifunovic, Srecko R. (2002). "Transition Metal Complexes with EDDA-Type Ligands-a Review". Synthesis and Reactivity in Inorganic and Metal-Organic Chemistry. 32: 1661–1717. doi:10.1081/SIM-120015086. S2CID 94409799.
- ^ Leon J. Halloran; Arlene L. Gillie; J. Ivan Legg (1978). "Ethylenediamine- N,N ′-Diacetic Acid Complexes of Cobalt(III)". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 18. pp. 103–111. doi:10.1002/9780470132494.ch17. ISBN 978-0-470-13249-4.