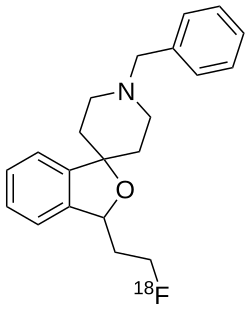
Fluspidine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | [18F]-Fluspidine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H24FNO |
| Molar mass | 325.427 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Fluspidine is a fluorine-18 (18F) labeled radiotracer used in positron emission tomography (PET) scans to image σ1 (sigma-1) receptors in the brain and other tissues. Sigma-1 receptors are proteins involved in many neurological and psychiatric processes. They have been linked to pain modulation, psychosis, Alzheimer's disease, and depression.[1]
Chemical properties
Fluspidine is a small organic compound with a spirocyclic structure. A 2-fluoroethyl group on the molecule carries the fluorine-18. The compound exists as two mirror image enantiomers, called (R)-fluspidine and (S)-fluspidine. These enantiomers have slightly different properties: (R)-fluspidine has about 4-fold higher affinity for the σ₁ receptor than (S)-fluspidine, but (S)-fluspidine is metabolically more stable in the body.[2]
References
- ^ Ludwig FA, Laurini E, Schmidt J, Pricl S, Deuther-Conrad W, Wünsch B (January 2024). "[18F]Fluspidine-A PET Tracer for Imaging of σ1 Receptors in the Central Nervous System". Pharmaceuticals. 17 (2): 166. doi:10.3390/ph17020166. PMC 10892410. PMID 38399380.
- ^ Brust P, Deuther-Conrad W, Becker G, Patt M, Donat CK, Stittsworth S, et al. (October 2014). "Distinctive in vivo kinetics of the new σ1 receptor ligands (R)-(+)- and (S)-(-)-18F-fluspidine in porcine brain". Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 55 (10): 1730–1736. doi:10.2967/jnumed.114.137562. PMID 25071097.