Formaldoxime
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-Hydroxymethanimine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.769 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
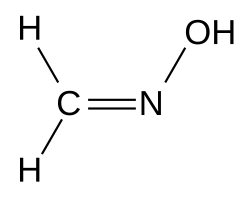
| H2C=N−OH | |
| Molar mass | 45.041 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Melting point | 2.5 °C (36.5 °F; 275.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 84 °C (183 °F; 357 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Formaldoxime is the organic compound with the formula H2C=N−OH. It is the oxime of formaldehyde. A colorless liquid, the pure compound tends to polymerize into a cyclic trimer. Aqueous solutions are stable as is the formaldoxime hydrochloride ([H2C=N(−H)(−OH)]+Cl−). It is a reagent in organic synthesis for the conversion of aryl diazonium salts to aryl aldehydes.[1]m
It is generated by combining hydroxylamine and formaldehyde.[2]
Synonyms
Source:[3]
- Formoxime
- Nitrone
- Formaldehyde oxime
- formaldoxim
- methylenenitrone
References
- ^ De Kimpe, Norbert (2001). "Formaldoxime". E-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rf023. ISBN 0-471-93623-5.
- ^ S. D. Jolad, S. Rajagopalan (1966). "2-Bromo-4-methylbenzaldehyde". Org. Synth. 46: 13. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.046.0013.
- ^ https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Formaldoxime#section=Depositor-Supplied-Synonyms&fullscreen=true