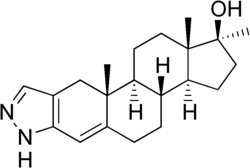
Hydroxystenozole
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | NSC-43194; 4-Dehydrostanozolol; 17α-Methyl-2'H-androsta-2,4-dieno[3,2-c]pyrazol-17β-ol |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H30N2O |
| Molar mass | 326.484 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Hydroxystenozole (INN), also known as 17α-methylandrost-4-eno[3,2-c]pyrazol-17β-ol, is an orally active androgen/anabolic steroid (AAS) and a 17α-alkylated derivative of testosterone that was described in the literature in 1967 but was never marketed.[1] It is closely related to stanozolol (17α-methyl-5α-androstano[3,2-c]pyrazol-17β-ol), differing from it only in hydrogenation (i.e., double bonds and their placement).[1]
References
- ^ a b Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. p. 668. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.