Aerial view of Mount Everest from the south. The peak rises over Lhotse , while Nuptse is the ridge on the left. There are at least 108 mountains on Earth with elevations of 7,200 m (23,622 ft; 4 mi) or greater above sea level . Of these, 14 are more than 8,000 m (26,247 ft; 5 mi).[ 1] Himalayas or the Karakoram mountain ranges located on the edge of the Indian Plate and Eurasian Plate in China , India , Nepal , and Pakistan .[ a]
Discussion
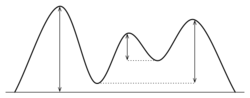
Figure demonstrating the concept of topographic prominence : The prominence of a peak is the height of the peak's summit above the lowest contour line encircling it and no higher summit. For example, vertical arrows show the topographic prominence of three peaks on an island. A dotted horizontal line links each peak (except the highest) to its key col . The dividing line between a mountain with multiple peaks and separate mountains is not always clear (see also Highest unclimbed mountain ). A popular and intuitive way to distinguish mountains from subsidiary peaks is by their height above the highest saddle connecting it to a higher summit, a measure called topographic prominence or re-ascent (the higher summit is called the "parent peak"). A common definition of a mountain is a summit with 300 m (984 ft) prominence. Alternatively, a relative prominence (prominence/height) is used (usually 7–8%) to reflect that in higher mountain ranges everything is on a larger scale. The table below lists the highest 100 summits with at least 500 m (1,640 ft) prominence, approximating a 7% relative prominence. A drawback of a prominence-based list is that it may exclude well-known or spectacular mountains that are connected via a high ridge to a taller summit, such as Eiger , Nuptse or Annapurna IV . A few such peaks and mountains with nearly sufficient prominence are included in this list, and given a rank of "S".
It is very unlikely that all given heights are correct to the nearest metre; indeed, the sea level is often problematic to define when a mountain is remote from the sea. Different sources often differ by many metres, and the heights given below may well differ from those elsewhere in this encyclopedia. As an extreme example, Ulugh Muztagh on the north Tibetan Plateau is often listed as 7,723 m (25,338 ft) to 7,754 m (25,440 ft), but appears to be only 6,973 m (22,877 ft) to 6,987 m (22,923 ft). Some mountains differ by more than 100 m (330 ft) on different maps, while even very thorough current measurements of Mount Everest range from 8,840 m (29,003 ft) to 8,849 m (29,032 ft). These discrepancies serve to emphasize the uncertainties in the listed heights.
Though some parts of the world, especially the most mountainous parts, have never been thoroughly mapped, it is unlikely that any mountains this high have been overlooked, because synthetic aperture radar can and has been used to measure elevations of most otherwise inaccessible places. Still, heights or prominences may be revised, so that the order of the list may change and even new mountains could enter the list over time. To be safe, the list has been extended to include all 7,200 m (23,622 ft) peaks.
The highest mountains above sea level are generally not the highest mountains above the surrounding terrain, also called the highest free-standing mountains. There is no precise definition of surrounding base, but Denali ,[ 2] Mount Kilimanjaro [ 3] Nanga Parbat [ 4]
The bases of mountain islands are below sea level, and given this consideration Mauna Kea (4,207 m (13,802 ft) above sea level) is the world 's tallest mountain and volcano , rising about 10,203 m (33,474 ft) from the Pacific Ocean floor. Mount Lamlam on Guam is periodically claimed to be among the world's highest mountains because it is adjacent to the Mariana Trench ; the most extreme claim is that, measured from Challenger Deep 313 kilometres (194 mi) away, Mount Lamlam is 11,530 metres (37,820 ft) tall.[ 5] [ 6] Ojos del Salado has the greatest rise on Earth : 13,420 m (44,029 ft) vertically to the summit from the bottom of the Atacama Trench , which is about 560 km (350 mi) away, although most of this rise is not part of the mountain.
The highest mountains are also not generally the most voluminous. Mauna Loa (4,169 m or 13,678 ft) is the largest mountain on Earth in terms of base area (about 5,200 km2 or 2,000 sq mi) and volume (about 42,000 km3 or 10,000 cu mi), although, due to the intergrade of lava from Kilauea , Hualalai and Mauna Kea , the volume can only be estimated based on surface area and height of the edifice. Mount Kilimanjaro is the largest non-shield volcano in terms of both base area (635 km2 or 245 sq mi) and volume (4,793 km3 or 1,150 cu mi). Mount Logan is the largest non-volcanic mountain in base area (311 km2 or 120 sq mi).
The highest mountains above sea level are also not those with peaks farthest from the centre of the Earth, because the shape of the Earth is not spherical. Sea level closer to the equator is several kilometres farther from the centre of the Earth. The summit of Chimborazo , Ecuador 's tallest mountain, is usually considered to be the farthest point from the Earth's centre, although the southern summit of Peru 's tallest mountain, Huascarán , is another contender.[ 7]
Geographical distribution
Number of mountain peaks [ a]
China
50
Pakistan
42
Nepal
32
India
27
Bhutan
5
Afghanistan
1
Kyrgyzstan
1
Tajikistan
1
Almost all mountains in the list are located in the Himalaya and Karakoram ranges to the south and west of the Tibetan plateau. All peaks 7,000 m (22,966 ft) or higher are located in East , Central or South Asia in a rectangle edged by Noshaq (7,492 m or 24,580 ft) on the Afghanistan–Pakistan border in the west, Jengish Chokusu (Tuōmù'ěr Fēng, 7,439 m or 24,406 ft) on the Kyrgyzstan –Xinjiang border to the north, Gongga Shan (Minya Konka, 7,556 m or 24,790 ft) in Sichuan to the east, and Kabru (7,412 m or 24,318 ft) on the Sikkim –Nepal border to the south.
As of May 2025, the highest peaks on three of the mountains—Gangkhar Puensum , Labuche Kang III and Tongshanjiabu , all located in Bhutan or China —have not been ascended. The most recent peak to have its first ever ascent is Karjiang , in China , on 13 August 2024.
The highest mountain outside of Asia is Aconcagua (6,961 m or 22,838 ft), the 189th highest in the world.[ 8]
List of highest peaks
List of Earth's highest peaks with their prominence and parent mountain
Rank[ i]
Mountain name(s)
Height[ ii]
Prominence[ iii]
Range
Coordinates[ iv]
Parent mountain [ v] First[ vi]
Country/
Photo
1
8,849 metres (29,032 ft)[ b]
8,849 metres (29,032 ft)
Mahalangur Himalaya
27°59′17″N 86°55′30″E / 27.9881°N 86.925°E / 27.9881; 86.925 (1. Mount Everest / Sagarmatha / Chomolungma / Zhumulangma (8848 m) ) —
1953
2
K2
8,611 metres (28,251 ft)
4,020 metres (13,190 ft)
Baltoro Karakoram
35°52′53″N 76°30′48″E / 35.88139°N 76.51333°E / 35.88139; 76.51333 (2. K2 / Qogir / Godwin Austen (8611 m) ) Mount Everest
1954
3
Kangchenjunga
8,586 metres (28,169 ft)
3,922 metres (12,867 ft)
Kangchenjunga Himalaya
27°42′12″N 88°08′51″E / 27.70333°N 88.14750°E / 27.70333; 88.14750 (3. Kangchenjunga (8586 m) ) Mount Everest
1955
4
Lhotse
8,516 metres (27,940 ft)
610 metres (2,000 ft)
Mahalangur Himalaya
27°57′42″N 86°55′59″E / 27.96167°N 86.93306°E / 27.96167; 86.93306 (4. Lhotse (8516 m) ) Mount Everest
1956
5
Makalu
8,485 metres (27,838 ft)
2,378 metres (7,802 ft)
Mahalangur Himalaya
27°53′23″N 87°05′20″E / 27.88972°N 87.08889°E / 27.88972; 87.08889 (5. Makalu (8485 m) ) Mount Everest
1955
6
Cho Oyu
8,188 metres (26,864 ft)[ d]
2,340 metres (7,680 ft)
Mahalangur Himalaya
28°05′39″N 86°39′39″E / 28.09417°N 86.66083°E / 28.09417; 86.66083 (6. Cho Oyu (8188 m) ) Mount Everest
1954
7
Dhaulagiri I
8,167 metres (26,795 ft)
3,357 metres (11,014 ft)
Dhaulagiri Himalaya
28°41′48″N 83°29′35″E / 28.69667°N 83.49306°E / 28.69667; 83.49306 (7. Dhaulagiri I (8167 m) ) K2
1960
Nepal
8
Manaslu
8,163 metres (26,781 ft)
3,092 metres (10,144 ft)
Manaslu Himalaya
28°33′00″N 84°33′35″E / 28.55000°N 84.55972°E / 28.55000; 84.55972 (8. Manaslu (8163 m) ) Cho Oyu
1956
Nepal
9
Nanga Parbat
8,126 metres (26,660 ft)
4,608 metres (15,118 ft)
Nanga Parbat Himalaya
35°14′14″N 74°35′21″E / 35.23722°N 74.58917°E / 35.23722; 74.58917 (9. Nanga Parbat (8126 m) ) Dhaulagiri
1953
Pakistan
10
Annapurna I
8,091 metres (26,545 ft)
2,984 metres (9,790 ft)
Annapurna Himalaya
28°35′44″N 83°49′13″E / 28.59556°N 83.82028°E / 28.59556; 83.82028 (10. Annapurna I (8091 m) ) Cho Oyu
1950
Nepal
11
8,080 metres (26,510 ft)
2,155 metres (7,070 ft)
Baltoro Karakoram
35°43′28″N 76°41′47″E / 35.72444°N 76.69639°E / 35.72444; 76.69639 (11. Gasherbrum I / Hidden Peak / K5 (8080 m) ) K2
1958
12
Broad Peak
8,051 metres (26,414 ft)
1,701 metres (5,581 ft)
Baltoro Karakoram
35°48′38″N 76°34′06″E / 35.81056°N 76.56833°E / 35.81056; 76.56833 (12. Broad Peak / K3 (8051 m) ) Gasherbrum I
1957
13
8,035 metres (26,362 ft)
1,524 metres (5,000 ft)
Baltoro Karakoram
35°45′28″N 76°39′12″E / 35.75778°N 76.65333°E / 35.75778; 76.65333 (13. Gasherbrum II / K4 (8035 m) ) Gasherbrum I
1956
14
8,027 metres (26,335 ft)
2,897 metres (9,505 ft)
Jugal Himalaya
28°21′12″N 85°46′43″E / 28.35333°N 85.77861°E / 28.35333; 85.77861 (14. Shishapangma (8027 m) ) Cho Oyu
1964
China
15
Gyachung Kang
7,952 metres (26,089 ft)
672 metres (2,205 ft)
Mahalangur Himalaya
28°05′53″N 86°44′42″E / 28.09806°N 86.74500°E / 28.09806; 86.74500 (15. Gyachung Kang (7952 m) ) Cho Oyu
1964
S
7,946 metres (26,070 ft)
355 metres (1,165 ft)
Baltoro Karakoram
35°45′33″N 76°38′30″E / 35.75917°N 76.64167°E / 35.75917; 76.64167 (Gasherbrum III (7946 m) ) Gasherbrum II
1975
16
Annapurna II
7,937 metres (26,040 ft)
2,437 metres (7,995 ft)
Annapurna Himalaya
28°32′05″N 84°07′19″E / 28.53472°N 84.12194°E / 28.53472; 84.12194 (16. Annapurna II (7937 m) ) Annapurna I
1960
Nepal
17
7,932 metres (26,024 ft)
712 metres (2,336 ft)
Baltoro Karakoram
35°45′38″N 76°36′58″E / 35.76056°N 76.61611°E / 35.76056; 76.61611 (17. Gasherbrum IV (7932 m) ) Gasherbrum III
1958
Pakistan
18
Himalchuli
7,893 metres (25,896 ft)
1,633 metres (5,358 ft)
Manaslu Himalaya
28°26′12″N 84°38′23″E / 28.43667°N 84.63972°E / 28.43667; 84.63972 (18. Himalchuli (7893 m) ) Manaslu
1960
Nepal
19
Distaghil Sar
7,884 metres (25,866 ft)
2,525 metres (8,284 ft)
Hispar Karakoram
36°19′33″N 75°11′16″E / 36.32583°N 75.18778°E / 36.32583; 75.18778 (19. Distaghil Sar (7884 m) ) K2
1960
Pakistan
20
Ngadi Chuli
7,871 metres (25,823 ft)
1,011 metres (3,317 ft)
Manaslu Himalaya
28°30′12″N 84°34′00″E / 28.50333°N 84.56667°E / 28.50333; 84.56667 (20. Ngadi Chuli (7871 m) ) Manaslu
1979
Nepal
S
Nuptse
7,864 metres (25,801 ft)
305 metres (1,001 ft)
Mahalangur Himalaya
27°58′03″N 86°53′13″E / 27.96750°N 86.88694°E / 27.96750; 86.88694 (Nuptse (7864 m) ) Lhotse
1961
Nepal
21
Khunyang Chhish
7,823 metres (25,666 ft)
1,765 metres (5,791 ft)
Hispar Karakoram
36°12′19″N 75°12′28″E / 36.20528°N 75.20778°E / 36.20528; 75.20778 (21. Khunyang Chhish (7823 m) ) Distaghil Sar
1971
Pakistan
22
7,821 metres (25,659 ft)
2,457 metres (8,061 ft)
Masherbrum Karakoram
35°38′28″N 76°18′21″E / 35.64111°N 76.30583°E / 35.64111; 76.30583 (22. Masherbrum / K1 (7821 m) ) Gasherbrum I
1960
Pakistan
23
Nanda Devi
7,817 metres (25,646 ft)
3,139 metres (10,299 ft)
Garhwal Himalaya
30°22′33″N 79°58′15″E / 30.37583°N 79.97083°E / 30.37583; 79.97083 (23. Nanda Devi (7816 m) ) Dhaulagiri
1936
India
24
Chomo Lonzo
7,804 metres (25,604 ft)
590 metres (1,940 ft)
Mahalangur Himalaya
27°55′50″N 87°06′28″E / 27.93056°N 87.10778°E / 27.93056; 87.10778 (24. Chomo Lonzo (7804 m) ) Makalu
1954
China
25
Batura Sar
7,795 metres (25,574 ft)
3,118 metres (10,230 ft)
Batura Karakoram
36°30′37″N 74°31′21″E / 36.51028°N 74.52250°E / 36.51028; 74.52250 (25. Batura Sar (7795 m) ) Distaghil Sar
1976
Pakistan
26
Rakaposhi
7,788 metres (25,551 ft)
2,818 metres (9,245 ft)
Rakaposhi-Haramosh Karakoram
36°08′33″N 74°29′22″E / 36.14250°N 74.48944°E / 36.14250; 74.48944 (26. Rakaposhi (7788 m) ) Khunyang Chhish
1958
Pakistan
27
Namcha Barwa
7,782 metres (25,531 ft)
4,106 metres (13,471 ft)
Assam Himalaya
29°37′52″N 95°03′19″E / 29.63111°N 95.05528°E / 29.63111; 95.05528 (27. Namcha Barwa (7782 m) ) Kangchenjunga
1992
China
28
Kanjut Sar
7,760 metres (25,460 ft)
1,660 metres (5,450 ft)
Hispar Karakoram
36°12′20″N 75°25′01″E / 36.20556°N 75.41694°E / 36.20556; 75.41694 (28. Kanjut Sar (7760 m) ) Khunyang Chhish
1959
Pakistan
29
Kamet
7,756 metres (25,446 ft)
2,825 metres (9,268 ft)
Garhwal Himalaya
30°55′12″N 79°35′30″E / 30.92000°N 79.59167°E / 30.92000; 79.59167 (29. Kamet (7756 m) ) Nanda Devi
1931
India
30
Dhaulagiri II
7,751 metres (25,430 ft)
2,397 metres (7,864 ft)
Dhaulagiri Himalaya
28°45′46″N 83°23′18″E / 28.76278°N 83.38833°E / 28.76278; 83.38833 (30. Dhaulagiri II (7751 m) ) Dhaulagiri
1971
Nepal
31
7,742 metres (25,400 ft)
2,160 metres (7,090 ft)
Saltoro Karakoram
35°23′57″N 76°50′53″E / 35.39917°N 76.84806°E / 35.39917; 76.84806 (31. Saltoro Kangri / K10 (7742 m) ) Gasherbrum I
1962
32
7,711 metres (25,299 ft)
1,036 metres (3,399 ft)
Kangchenjunga Himalaya
27°40′56″N 88°02′40″E / 27.68222°N 88.04444°E / 27.68222; 88.04444 (32. Jannu (7711 m) ) Kangchenjunga
1962
Nepal
33
Tirich Mir
7,708 metres (25,289 ft)
3,910 metres (12,830 ft)
Hindu Kush
36°15′19″N 71°50′30″E / 36.25528°N 71.84167°E / 36.25528; 71.84167 (33. Tirich Mir (7708 m) ) Batura Sar
1950
Pakistan
S
Molamenqing
7,703 metres (25,272 ft)
433 metres (1,421 ft)
Langtang Himalaya
28°21′18″N 85°48′35″E / 28.35500°N 85.80972°E / 28.35500; 85.80972 (Molamenqing (7703 m) ) Shishapangma
1981
China
34
Gurla Mandhata
7,694 metres (25,243 ft)
2,788 metres (9,147 ft)
Nalakankar Himalaya
30°26′19″N 81°17′48″E / 30.43861°N 81.29667°E / 30.43861; 81.29667 (34. Gurla Mandhata (7694 m) ) Dhaulagiri
1985
China
35
7,672 metres (25,171 ft)
2,304 metres (7,559 ft)
Saser Karakoram
34°52′00″N 77°45′09″E / 34.86667°N 77.75250°E / 34.86667; 77.75250 (35. Saser Kangri I / K22 (7672 m) ) Gasherbrum I
1973
India
36
Chogolisa
7,665 metres (25,148 ft)
1,624 metres (5,328 ft)
Masherbrum Karakoram
35°36′47″N 76°34′29″E / 35.61306°N 76.57472°E / 35.61306; 76.57472 (36. Chogolisa (7665 m) ) Gasherbrum I
1975
Pakistan
S
Dhaulagiri IV
7,661 metres (25,135 ft)
469 metres (1,539 ft)
Dhaulagiri Himalaya
28°44′09″N 83°18′55″E / 28.73583°N 83.31528°E / 28.73583; 83.31528 (Dhaulagiri IV (7661 m) ) Dhaulagiri II
1975
Nepal
37
Kongur Tagh
7,649 metres (25,095 ft)
3,585 metres (11,762 ft)
Kongur Shan (Eastern Pamirs )
38°35′36″N 75°18′48″E / 38.59333°N 75.31333°E / 38.59333; 75.31333 (37. Kongur Tagh (7649 m) ) Distaghil Sar
1981
China
S
Dhaulagiri V
7,618 metres (24,993 ft)
340 metres (1,120 ft)
Dhaulagiri Himalaya
28°44′02″N 83°21′41″E / 28.73389°N 83.36139°E / 28.73389; 83.36139 (Dhaulagiri V (7618 m) ) Dhaulagiri IV
1975
Nepal
38
Shispare
7,611 metres (24,970 ft)
1,240 metres (4,070 ft)
Batura Karakoram
36°26′26″N 74°40′51″E / 36.44056°N 74.68083°E / 36.44056; 74.68083 (38. Shispare (7611 m) ) Batura Sar
1974
Pakistan
39
Trivor
7,577 metres (24,859 ft)
997 metres (3,271 ft)
Hispar Karakoram
36°17′15″N 75°05′06″E / 36.28750°N 75.08500°E / 36.28750; 75.08500 (39. Trivor (7577 m) ) Distaghil Sar
1960
Pakistan
40
Gangkhar Puensum
7,570 metres (24,840 ft)
2,995 metres (9,826 ft)
Kula Kangri Himalaya
28°02′50″N 90°27′19″E / 28.04722°N 90.45528°E / 28.04722; 90.45528 (40. Gangkhar Puensum (7570 m) ) Kangchenjunga
none
41
7,556 metres (24,790 ft)
3,642 metres (11,949 ft)
Daxue Mountains (Hengduan Shan )
29°35′43″N 101°52′47″E / 29.59528°N 101.87972°E / 29.59528; 101.87972 (41. Gongga Shan / Minya Konka (7556 m) ) Mount Everest
1932
China
42
Annapurna III
7,555 metres (24,787 ft)
703 metres (2,306 ft)
Annapurna Himalaya
28°35′06″N 83°59′24″E / 28.58500°N 83.99000°E / 28.58500; 83.99000 (42. Annapurna III (7555 m) ) Annapurna I
1961
Nepal
43
Skyang Kangri
7,545 metres (24,754 ft)
1,085 metres (3,560 ft)
Baltoro Karakoram
35°55′35″N 76°34′03″E / 35.92639°N 76.56750°E / 35.92639; 76.56750 (43. Skyang Kangri (7545 m) ) K2
1976
Pakistan , China
44
Changtse
7,543 metres (24,747 ft)[ 16]
514 metres (1,686 ft)
Mahalangur Himalaya
28°01′29″N 86°54′51″E / 28.02472°N 86.91417°E / 28.02472; 86.91417 (44. Changtse (7543 m) ) Mount Everest
1982
China
45
Kula Kangri
7,538 metres (24,731 ft)
1,654 metres (5,427 ft)
Kula Kangri Himalaya
28°13′37″N 90°36′59″E / 28.22694°N 90.61639°E / 28.22694; 90.61639 (45. Kula Kangri (7538 m) ) Gangkhar Puensum
1986
[ e]
46
Kongur Tiube
7,530 metres (24,700 ft)
840 metres (2,760 ft)
Kongur Shan (Eastern Pamirs )
38°36′57″N 75°11′45″E / 38.61583°N 75.19583°E / 38.61583; 75.19583 (46. Kongur Tiube (7530 m) ) Kongur Tagh
1956
China
S
Annapurna IV
7,525 metres (24,688 ft)
255 metres (837 ft)
Annapurna Himalaya
28°32′15″N 84°4′58″E / 28.53750°N 84.08278°E / 28.53750; 84.08278 (Annapurna IV (7,525 m) ) Annapurna
1955
Nepal
47
Mamostong Kangri
7,516 metres (24,659 ft)
1,803 metres (5,915 ft)
Rimo Karakoram
35°08′31″N 77°34′39″E / 35.14194°N 77.57750°E / 35.14194; 77.57750 (47. Mamostong Kangri (7516 m) ) Gasherbrum I
1984
India
48
Saser Kangri II E
7,513 metres (24,649 ft)
1,458 metres (4,783 ft)
Saser Karakoram
34°48′17″N 77°48′24″E / 34.80472°N 77.80667°E / 34.80472; 77.80667 (48. Saser Kangri II E (7513 m) ) Saser Kangri I
2011[ 17] [ f]
India
49
Muztagh Ata
7,509 metres (24,636 ft)
2,698 metres (8,852 ft)
Muztagata (Eastern Pamirs )
38°16′33″N 75°06′58″E / 38.27583°N 75.11611°E / 38.27583; 75.11611 (49. Muztagh Ata (7546 m) ) Kongur Tagh
1956
China
50
Ismoil Somoni Peak
7,495 metres (24,590 ft)
3,402 metres (11,161 ft)
Pamir (Academy of Sciences Range )
38°56′35″N 72°00′57″E / 38.94306°N 72.01583°E / 38.94306; 72.01583 (50. Ismoil Somoni Peak (7495 m) ) Muztagh Ata
1933
Tajikistan
51
Saser Kangri III
7,495 metres (24,590 ft)
835 metres (2,740 ft)
Saser Karakoram
34°50′44″N 77°47′06″E / 34.84556°N 77.78500°E / 34.84556; 77.78500 (51. Saser Kangri III (7495 m) ) Saser Kangri I
1986
India [ g]
52
Noshaq
7,492 metres (24,580 ft)
2,024 metres (6,640 ft)
Hindu Kush
36°25′56″N 71°49′43″E / 36.43222°N 71.82861°E / 36.43222; 71.82861 (52. Noshaq (7492 m) ) Tirich Mir
1960
53
Pumari Chhish
7,492 metres (24,580 ft)
884 metres (2,900 ft)
Hispar Karakoram
36°12′41″N 75°15′01″E / 36.21139°N 75.25028°E / 36.21139; 75.25028 (53. Pumari Chhish (7492 m) ) Khunyang Chhish
1979
Pakistan
54
Passu Sar
7,476 metres (24,528 ft)
647 metres (2,123 ft)
Batura Karakoram
36°29′16″N 74°35′16″E / 36.48778°N 74.58778°E / 36.48778; 74.58778 (54. Passu Sar (7476 m) ) Batura Sar
1994
Pakistan
55
Yukshin Gardan Sar
7,469 metres (24,505 ft)
1,374 metres (4,508 ft)
Hispar Karakoram
36°15′04″N 75°22′29″E / 36.25111°N 75.37472°E / 36.25111; 75.37472 (55. Yukshin Gardan Sar (7469 m) ) Pumari Chhish
1984
Pakistan
56
Teram Kangri I
7,462 metres (24,482 ft)
1,703 metres (5,587 ft)
Siachen Karakoram
35°34′48″N 77°04′42″E / 35.58000°N 77.07833°E / 35.58000; 77.07833 (56. Teram Kangri I (7462 m) ) Gasherbrum I
1975
[ h] [ i] [ g]
57
Jongsong Peak
7,462 metres (24,482 ft)
1,298 metres (4,259 ft)
Kangchenjunga Himalaya
27°52′54″N 88°08′09″E / 27.88167°N 88.13583°E / 27.88167; 88.13583 (57. Jongsong Peak (7462 m) ) Kangchenjunga
1930
58
Malubiting
7,458 metres (24,469 ft)
2,193 metres (7,195 ft)
Rakaposhi-Haramosh Karakoram
36°00′12″N 74°52′31″E / 36.00333°N 74.87528°E / 36.00333; 74.87528 (58. Malubiting (7458 m) ) Rakaposhi
1971
Pakistan
59
Gangapurna
7,455 metres (24,459 ft)
563 metres (1,847 ft)
Annapurna Himalaya
28°36′18″N 83°57′49″E / 28.60500°N 83.96361°E / 28.60500; 83.96361 (59. Gangapurna (7455 m) ) Annapurna III
1965
Nepal
60
7,439 metres (24,406 ft)
4,148 metres (13,609 ft)
Tian Shan
42°02′05″N 80°07′47″E / 42.03472°N 80.12972°E / 42.03472; 80.12972 (60. Jengish Chokusu / Tömür / Pk Pobeda (7439 m) ) Ismail Samani Peak
1956
S
7,434 metres (24,390 ft)
229 metres (751 ft)
Garhwal Himalaya
30°22′00″N 79°59′40″E / 30.36667°N 79.99444°E / 30.36667; 79.99444 (Sunanda Devi (7434 m) ) Nanda Devi
1939
India
61
K12
7,428 metres (24,370 ft)
1,978 metres (6,490 ft)
Saltoro Karakoram
35°17′45″N 77°01′20″E / 35.29583°N 77.02222°E / 35.29583; 77.02222 (61. K12 (7428 m) ) Saltoro Kangri
1974
62
7,422 metres (24,350 ft)
2,352 metres (7,717 ft)
Ganesh Himalaya
28°23′29″N 85°07′38″E / 28.39139°N 85.12722°E / 28.39139; 85.12722 (62. Yangra / Ganesh I (7422 m) ) Shishapangma
1955
63
Sia Kangri
7,422 metres (24,350 ft)
642 metres (2,106 ft)
Siachen Karakoram
35°39′48″N 76°45′42″E / 35.66333°N 76.76167°E / 35.66333; 76.76167 (63. Sia Kangri (7422 m) ) Gasherbrum I
1934
64
Momhil Sar
7,414 metres (24,324 ft)
907 metres (2,976 ft)
Hispar Karakoram
36°19′04″N 75°02′11″E / 36.31778°N 75.03639°E / 36.31778; 75.03639 (64. Momhil Sar (7414 m) ) Trivor
1964
Pakistan
65
Kabru N
7,412 metres (24,318 ft)
720 metres (2,360 ft)
Kangchenjunga Himalaya
27°38′02″N 88°07′00″E / 27.63389°N 88.11667°E / 27.63389; 88.11667 (65. Kabru N (7412 m) ) Kangchenjunga
1994
66
Skil Brum
7,410 metres (24,310 ft)
1,152 metres (3,780 ft)
Baltoro Karakoram
35°51′03″N 76°25′43″E / 35.85083°N 76.42861°E / 35.85083; 76.42861 (66. Skil Brum (7410 m) ) K2
1957
Pakistan
67
Haramosh Peak
7,409 metres (24,308 ft)
2,277 metres (7,470 ft)
Rakaposhi-Haramosh Karakoram
35°50′24″N 74°53′51″E / 35.84000°N 74.89750°E / 35.84000; 74.89750 (67. Haramosh Peak (7409 m) ) Malubiting
1958
Pakistan
68
Istor-o-Nal
7,403 metres (24,288 ft)
1,043 metres (3,422 ft)
Hindu Kush
36°22′32″N 71°53′54″E / 36.37556°N 71.89833°E / 36.37556; 71.89833 (68. Istor-o-Nal (7403 m) ) Noshaq
1969
Pakistan
69
Ghent Kangri
7,401 metres (24,281 ft)
1,493 metres (4,898 ft)
Saltoro Karakoram
35°31′04″N 76°48′02″E / 35.51778°N 76.80056°E / 35.51778; 76.80056 (69. Ghent Kangri (7401 m) ) Saltoro Kangri
1961
70
Ultar
7,388 metres (24,239 ft)
688 metres (2,257 ft)
Batura Karakoram
36°23′27″N 74°43′00″E / 36.39083°N 74.71667°E / 36.39083; 74.71667 (70. Ultar (7388 m) ) Shispare
1996
Pakistan
71
Rimo I
7,385 metres (24,229 ft)
1,428 metres (4,685 ft)
Rimo Karakoram
35°21′18″N 77°22′08″E / 35.35500°N 77.36889°E / 35.35500; 77.36889 (71. Rimo I (7385 m) ) Teram Kangri I
1988
India
72
Churen Himal
7,385 metres (24,229 ft)
650 metres (2,130 ft)
Dhaulagiri Himalaya
28°44′05″N 83°13′03″E / 28.73472°N 83.21750°E / 28.73472; 83.21750 (72. Churen Himal (7385 m) ) Dhaulagiri IV
1970
Nepal
73
Teram Kangri III
7,382 metres (24,219 ft)
520 metres (1,710 ft)
Siachen Karakoram
35°35′59″N 77°02′53″E / 35.59972°N 77.04806°E / 35.59972; 77.04806 (73. Teram Kangri III (7382 m) ) Teram Kangri I
1979
[ h] [ i] [ g]
74
Sherpi Kangri
7,380 metres (24,210 ft)
1,320 metres (4,330 ft)
Saltoro Karakoram
35°27′58″N 76°46′53″E / 35.46611°N 76.78139°E / 35.46611; 76.78139 (74. Sherpi Kangri (7380 m) ) Ghent Kangri
1976
75
Labuche Kang
7,367 metres (24,170 ft)
1,957 metres (6,421 ft)
Labuche Himalaya
28°18′15″N 86°21′03″E / 28.30417°N 86.35083°E / 28.30417; 86.35083 (75. Labuche Kang (7367 m) ) Cho Oyu
1987
China
76
Kirat Chuli
7,362 metres (24,154 ft)
1,168 metres (3,832 ft)
Kangchenjunga Himalaya
27°47′16″N 88°11′43″E / 27.78778°N 88.19528°E / 27.78778; 88.19528 (76. Kirat Chuli (7362 m) ) Kangchenjunga
1939
S
Abi Gamin
7,355 metres (24,131 ft)
217 metres (712 ft)
Garhwal Himalaya
30°55′57″N 79°36′09″E / 30.93250°N 79.60250°E / 30.93250; 79.60250 (Abi Gamin (7355 m) ) Kamet
1950
S
7,350 metres (24,110 ft)
432 metres (1,417 ft)
Kangchenjunga Himalaya
27°44′27″N 88°09′31″E / 27.74083°N 88.15861°E / 27.74083; 88.15861 (Gimmigela / The Twins (7350 m) ) Kangchenjunga
1994
S
Nangpai Gosum
7,350 metres (24,110 ft)
427 metres (1,401 ft)
Mahalangur Himalaya
28°04′24″N 86°36′51″E / 28.07333°N 86.61417°E / 28.07333; 86.61417 (Nangpai Gosum (7350 m) ) Cho Oyu
1986
77
Saraghrar
7,349 metres (24,111 ft)
1,979 metres (6,493 ft)
Hindu Kush
36°32′51″N 72°06′54″E / 36.54750°N 72.11500°E / 36.54750; 72.11500 (77. Saraghrar (7349 m) ) Noshaq
1959
Pakistan
S
Talung
7,349 metres (24,111 ft)
366 metres (1,201 ft)
Kangchenjunga Himalaya
27°39′18″N 88°07′51″E / 27.65500°N 88.13083°E / 27.65500; 88.13083 (Talung (7349 m) ) Kabru
1964
78
7,326 metres (24,035 ft)
2,341 metres (7,680 ft)
Jomolhari Himalaya
27°49′36″N 89°16′04″E / 27.82667°N 89.26778°E / 27.82667; 89.26778 (78. Jomolhari (7326 m) ) Gangkhar Puensum
1937
79
Chamlang
7,321 metres (24,019 ft)
1,241 metres (4,072 ft)
Mahalangur Himalaya
27°46′30″N 86°58′47″E / 27.77500°N 86.97972°E / 27.77500; 86.97972 (79. Chamlang (7321 m) ) Lhotse
1961
Nepal
80
Chongtar
7,315 metres (23,999 ft)
1,295 metres (4,249 ft)
Baltoro Karakoram
35°54′55″N 76°25′45″E / 35.91528°N 76.42917°E / 35.91528; 76.42917 (80. Chongtar (7315 m) ) Skil Brum
1994
China [ h]
81
Baltoro Kangri
7,312 metres (23,990 ft)
1,140 metres (3,740 ft)
Masherbrum Karakoram
35°38′21″N 76°40′24″E / 35.63917°N 76.67333°E / 35.63917; 76.67333 (81. Baltoro Kangri (7312 m) ) Chogolisa
1963
Pakistan
82
Siguang Ri
7,309 metres (23,980 ft)
669 metres (2,195 ft)
Mahalangur Himalaya
28°08′50″N 86°41′06″E / 28.14722°N 86.68500°E / 28.14722; 86.68500 (82. Siguang Ri (7309 m) ) Cho Oyu
1989
China
83
7,295 metres (23,934 ft)
1,919 metres (6,296 ft)
Yengisogat Karakoram
36°06′24″N 76°12′21″E / 36.10667°N 76.20583°E / 36.10667; 76.20583 (83. The Crown / Huang Guan (7295 m) ) Skil Brum (K2 )
1993
China [ h]
84
Gyala Peri
7,294 metres (23,930 ft)
2,942 metres (9,652 ft)
Assam Himalaya
29°48′52″N 94°58′07″E / 29.81444°N 94.96861°E / 29.81444; 94.96861 (84. Gyala Peri (7294 m) ) Mount Everest
1986
China
85
Porong Ri
7,292 metres (23,924 ft)
512 metres (1,680 ft)
Langtang Himalaya
28°23′22″N 85°43′12″E / 28.38944°N 85.72000°E / 28.38944; 85.72000 (85. Porong Ri (7292 m) ) Shishapangma
1982
China
86
7,285 metres (23,901 ft)
1,891 metres (6,204 ft)
Panmah Karakoram
35°56′51″N 75°45′12″E / 35.94750°N 75.75333°E / 35.94750; 75.75333 (86. Baintha Brakk / The Ogre (7285 m) ) Kanjut Sar
1977
Pakistan
87
Yutmaru Sar
7,283 metres (23,894 ft)
680 metres (2,230 ft)
Hispar Karakoram
36°13′35″N 75°22′02″E / 36.22639°N 75.36722°E / 36.22639; 75.36722 (87. Yutmaru Sar (7283 m) ) Yukshin Gardan Sar
1980
Pakistan
88
7,282 metres (23,891 ft)
1,962 metres (6,437 ft)
Masherbrum Karakoram
35°25′06″N 76°33′06″E / 35.41833°N 76.55167°E / 35.41833; 76.55167 (88. Baltistan Peak / K6 (7282 m) ) Chogolisa
1970
Pakistan
89
7,281 metres (23,888 ft)
1,345 metres (4,413 ft)
Himalaya
28°33′03″N 85°32′44″E / 28.55083°N 85.54556°E / 28.55083; 85.54556 (89. Kangpenqing / Gang Benchhen (7281 m) ) Shishapangma
1982
China
90
Muztagh Tower
7,276 metres (23,871 ft)
1,710 metres (5,610 ft)
Baltoro Karakoram
35°49′40″N 76°21′40″E / 35.82778°N 76.36111°E / 35.82778; 76.36111 (90. Muztagh Tower (7276 m) ) Skil Brum
1956
91
Mana Peak
7,272 metres (23,858 ft)
732 metres (2,402 ft)
Garhwal Himalaya
30°52′50″N 79°36′55″E / 30.88056°N 79.61528°E / 30.88056; 79.61528 (91. Mana Peak (7272 m) ) Kamet
1937
India
S
Dhaulagiri VI
7,268 metres (23,845 ft)
488 metres (1,601 ft)
Dhaulagiri Himalaya
28°42′31″N 83°16′27″E / 28.70861°N 83.27417°E / 28.70861; 83.27417 (Dhaulagiri VI (7268 m) ) Dhaulagiri IV
1970
Nepal
92
Diran
7,266 metres (23,839 ft)
1,329 metres (4,360 ft)
Rakaposhi-Haramosh Karakoram
36°07′13″N 74°39′42″E / 36.12028°N 74.66167°E / 36.12028; 74.66167 (92. Diran (7266 m) ) Malubiting
1968
Pakistan
93
7,250 metres (23,790 ft)[ j]
570 metres (1,870 ft)
Labuche Himalaya
28°18′05″N 86°23′02″E / 28.30139°N 86.38389°E / 28.30139; 86.38389 (93. Labuche Kang III / East (7250 m) ) Labuche Himalaya
none
China
94
Putha Hiunchuli
7,246 metres (23,773 ft)
1,151 metres (3,776 ft)
Dhaulagiri Himalaya
28°44′52″N 83°08′46″E / 28.74778°N 83.14611°E / 28.74778; 83.14611 (94. Putha Hiunchuli (7246 m) ) Churen Himal
1954
Nepal
95
Apsarasas Kangri
7,245 metres (23,770 ft)
607 metres (1,991 ft)
Siachen Karakoram
35°32′19″N 77°08′55″E / 35.53861°N 77.14861°E / 35.53861; 77.14861 (95. Apsarasas Kangri (7245 m) ) Teram Kangri I
1976
[ h] [ i] [ g]
96
Mukut Parbat
7,242 metres (23,760 ft)
683 metres (2,241 ft)
Garhwal Himalaya
30°56′57″N 79°34′12″E / 30.94917°N 79.57000°E / 30.94917; 79.57000 (96. Mukut Parbat (7242 m) ) Kamet
1951
97
Rimo III
7,233 metres (23,730 ft)
613 metres (2,011 ft)
Rimo Karakoram
35°22′31″N 77°21′42″E / 35.37528°N 77.36167°E / 35.37528; 77.36167 (97. Rimo III (7233 m) ) Rimo I
1985
India [ k] [ g]
98
Langtang Lirung
7,227 metres (23,711 ft)
1,534 metres (5,033 ft)
Langtang Himalaya
28°15′22″N 85°31′01″E / 28.25611°N 85.51694°E / 28.25611; 85.51694 (98. Langtang Lirung (7227 m) ) Shishapangma
1978
Nepal
99
Karjiang
7,221 metres (23,691 ft)
895 metres (2,936 ft)
Kula Kangri Himalaya
28°15′27″N 90°38′49″E / 28.25750°N 90.64694°E / 28.25750; 90.64694 (99. Karjiang (7221 m) ) Kula Kangri
2024
China
100
Annapurna Dakshin (Annapurna South)
7,219 metres (23,684 ft)
769 metres (2,523 ft)
Annapurna Himalaya
28°31′06″N 83°48′22″E / 28.51833°N 83.80611°E / 28.51833; 83.80611 (100. Annapurna Dakshin (7219 m) ) Annapurna
1964
Nepal
101
Khartaphu
7,213 metres (23,665 ft)
712 metres (2,336 ft)
Mahalangur Himalaya
28°03′49″N 86°58′39″E / 28.06361°N 86.97750°E / 28.06361; 86.97750 (101. Khartaphu (7213 m) ) Mount Everest
1935
China
102
Tongshanjiabu [ 18] 7,207 metres (23,645 ft)
1,757 metres (5,764 ft)
Lunana Himalaya
28°11′12″N 89°57′27″E / 28.18667°N 89.95750°E / 28.18667; 89.95750 (102. Tongshanjiabu (7207 m) ) Gangkhar Puensum
none
[ l]
103
Malangutti Sar
7,207 metres (23,645 ft)
507 metres (1,663 ft)
Hispar Karakoram
36°21′47″N 75°08′57″E / 36.36306°N 75.14917°E / 36.36306; 75.14917 (103. Malangutti Sar (7207 m) ) Distaghil Sar
1985
Pakistan [ c]
104
7,206 metres (23,642 ft)
2,160 metres (7,090 ft)
Nagarze Himalaya
28°56′48″N 90°10′42″E / 28.94667°N 90.17833°E / 28.94667; 90.17833 (104. Noijin Kangsang / Norin Kang (7206 m) ) Gangkhar Puensum
1986
China
105
Langtang Ri
7,205 metres (23,638 ft)
665 metres (2,182 ft)
Langtang Himalaya
28°22′53″N 85°41′01″E / 28.38139°N 85.68361°E / 28.38139; 85.68361 (105. Langtang Ri (7205 m) ) Shishapangma
1981
106
7,204 metres (23,635 ft)
1,244 metres (4,081 ft)
Lunana Himalaya
28°09′24″N 90°04′15″E / 28.15667°N 90.07083°E / 28.15667; 90.07083 (106. Kangphu Kang (7204 m) ) Tongshanjiabu
2002
107
Singhi Kangri
7,202 metres (23,629 ft)
730 metres (2,400 ft)
Siachen Karakoram
35°35′59″N 76°59′01″E / 35.59972°N 76.98361°E / 35.59972; 76.98361 (107. Singhi Kangri (7202 m) ) Teram Kangri III
1976
[ h] [ i] [ g]
108
Lupghar Sar
7,200 metres (23,600 ft)
730 metres (2,400 ft)
Hispar Karakoram
36°21′01″N 75°02′13″E / 36.35028°N 75.03694°E / 36.35028; 75.03694 (108. Lupghar Sar (7200 m) ) Momhil Sar
1979
Pakistan [ c]
Gallery
See also
Notes
^ Peaks which are considered sub-prominences are given a rank of "S".
^ For Nepal, the heights indicated on the Nepal Topographic Maps are followed. For China and the Baltoro Karakoram, the heights are those of Mi Desheng's "The Maps of Snow Mountains in China". For the Hispar Karakoram the heights on a Russian 1:100,000 topo map.[ 9] Neate (1990) .
^ Prominences over 1,500 m (4,900 ft) are from Peaklist.org,[ 10] [ 11]
^ Coordinates were established by comparing topographical maps with satellite images and SRTM -derived terrain maps. The terrain maps and satellite images often do not match exactly. An asterisk (*) indicates that the map and image are shifted by more than 100 m (330 ft) and/or that the landscapes around the summit do not match.
^ The first higher mountain beyond the key saddle with at least 500 m (1,600 ft) prominence itself.
^ The number of ascents and failed attempts up to 2004 is extracted from Alpine Club Himalayan Index.[ 12] eight-thousanders . For instance, up to 2004 Mount Everest was scaled 2,251 times by individuals.[ 13]
^ a b The sovereignty over the Kashmir region , containing much of the area of Karakoram and Western Himalayas, is disputed and the region is partly administered by India, Pakistan and China.
^ Given the large differences between multiple "definitive" measurements of Mount Everest , the height agreed by China and Nepal on 8 December 2020 8,848.86 m (29,031.7 ft) is used for the rounded values. For more information, see Mount Everest#Surveys .
^ a b c d Pakistan Gilgit-Baltistan region
^ Cho Oyu's height is 8,188 m (26,864 ft) according to the Nepal Survey's 1996 topographical map,[ 15]
^ Wholly claimed by China as a part of its Tibet Autonomous Region ; on the border with Bhutan according to Bhutan
^ The lower West peak, 2.5 km (1.6 mi) away, was climbed in 1984 and twice since.
^ a b c d e f In India's disputed Ladakh region, claimed by Pakistan
^ a b c d e f In the Trans-Karakoram or Shaksgam Tract , ceded by Pakistan from its disputed Gilgit-Baltistan region to China's Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region , claimed by India as a part of its Ladakh union territory
^ a b c d On the border of the Siachen Glacier area, which is controlled by India, but is also claimed by Pakistan
^ The height is unknown, but over 7,200 m (23,600 ft) on both Chinese and Russian maps of the area.
^ In the Siachen Glacier region controlled by India, but claimed by Pakistan
^ a b Wholly claimed by Bhutan, but on the border of the Tibet Autonomous Region according to China
References
^ Launchbury, Eleanor (2024-01-15). "The 10 Highest Mountains in the World - World Stats and Facts" . worldstatsandfacts.com . Retrieved 2024-02-14 . ^ "Denali, AK, Not Everest, is the Tallest Mountain on Land in the World" . SnowBrains . 15 August 2022. Retrieved 29 December 2022 .^ sutikshan (20 October 2020). "Mount Kilimanjaro The largest free standing mountain in the world, Take a geotourism around the African wonder" . thejerker.com . Retrieved 29 December 2022 . ^ "Tallest mountain face" . Guinness World Records. 2 December 2004. Retrieved 29 December 2022 .^ McMahon, Mary (January 23, 2021). "How do Scientists Determine the World's Tallest Mountain?" . Info Bloom . Retrieved March 13, 2021 . ^ Fichtl, Marcus (August 31, 2017). "Guam's Mount Lamlam technically world's tallest mountain, though most of it is underwater" . Stars and Stripes . Retrieved March 13, 2021 . ^ Krulwich, Robert (April 7, 2007). "The 'Highest' Spot on Earth?" . NPR . Retrieved 21 March 2009 . ^ "Mount Aconcagua" . worldatlas.org. 13 July 2021. Retrieved August 17, 2021 .^ "Hispar area: expedition reports and maps" . Archived from the original on 2008-04-27. Retrieved 2008-07-15 .^ "The Ultra Project Prominence Lists" . peaklist.org . Retrieved 2024-12-25 .^ Jurgalski, Eberhard; de Ferranti, Jonathan (2009-05-01). "High Asia - All mountains and main peaks above 6650 m" . ^ "Alpine Club Himalayan Index" .^ "Summits and Deaths by year" . Everesthistory.com .^ "K2" . Britannica .^ H8615 ^ The 1998 1:50,000 National Geographic map of Mount Everest has a height of 7,583 m (24,879 ft) for "Bei Peak" and 7,066 m (23,182 ft) for Bei'ao (North Col), giving a 517 m (1,696 ft) prominence. Mi Desheng's 1997 1:100,000 map of the Everest region has a 7,543 m (24,747 ft) summit and a 7,042 m (23,104 ft) indication near the col, not quite corresponding to the lowest pass. His 1975 1:50,000 version (in Chinese only) has Changtse at 7,580 m (24,870 ft) and North Col at 7,028 m (23,058 ft). All maps agree that the eastern summit is the highest.
^ "First Ascent of Saser Kangri II" . American Alpine Club. Archived from the original on 2011-09-30.^ The name and information about this summit was extracted from the May 2003 edition of Japanese Alpine News.
Sources
Desheng, Mi (1990s). The Maps of Snow Mountains in China . Chinese Academy of Sciences. Finnish Meteorological Inst. (1990s). Nepal Topographic Maps . Nepalese Survey Dept. "High Mountain Info". High Mountain Sports Magazine (now Climb Magazine) . Neate, Jill (1989). High Asia: An Illustrated History of the 7000 Metre Peaks . Seattle: The Mountaineers . ISBN 0-89886-238-8 . Soviet military 1:100,000 topographic maps (most from 1980 to 1981)
External links
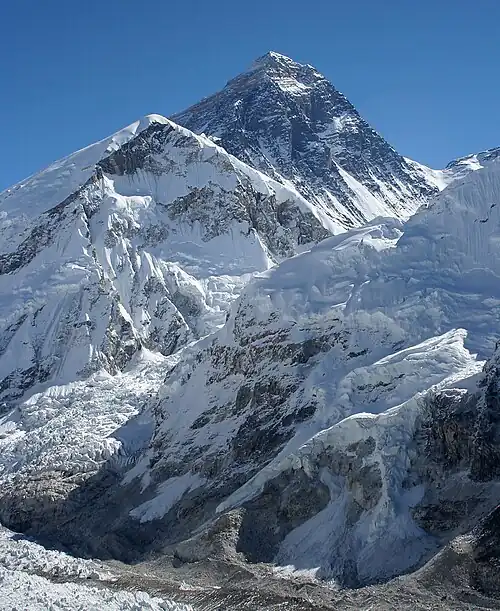
 The summit of Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth
The summit of Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth
 Kangchenjunga, the second-highest mountain of the Himalaya
Kangchenjunga, the second-highest mountain of the Himalaya Lhotse, the third-highest mountain of the Himalaya
Lhotse, the third-highest mountain of the Himalaya Makalu in the Himalaya
Makalu in the Himalaya Cho Oyu in the Himalaya
Cho Oyu in the Himalaya Dhaulagiri in the Himalaya
Dhaulagiri in the Himalaya Manaslu in the Himalaya
Manaslu in the Himalaya Nanga Parbat in the Himalaya
Nanga Parbat in the Himalaya Annapurna I in the Himalaya
Annapurna I in the Himalaya Gasherbrum I, the second-highest mountain of the Karakoram
Gasherbrum I, the second-highest mountain of the Karakoram Broad Peak, the third-highest mountain of the Karakoram
Broad Peak, the third-highest mountain of the Karakoram Gasherbrum II in the Karakoram
Gasherbrum II in the Karakoram Shishapangma in the Himalaya
Shishapangma in the Himalaya




.jpg)






.jpg)









.jpg)





_(25571147500)_(3to4).jpg)










_(25871754125).jpg)












.jpg)








