Lysine decarboxylase
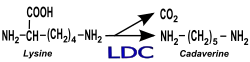 Cadaverine synthesis | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC no. | 4.1.1.18 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 9024-76-4 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The enzyme Lysine decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.18) converts lysine to cadaverine.[1][2]
Abbreviated as Ldc, the enzyme is involved in acid-stress response in Enterobacteria. The mode of action is the proton consumption, thereby reducing the overall acidity of its environnement.
References
- ^ Gale EF, Epps HM (1944). "Studies on bacterial amino-acid decarboxylases: 1. l(+)-lysine decarboxylase". Biochem. J. 38 (3): 232–42. doi:10.1042/bj0380232. PMC 1258073. PMID 16747785.
- ^ Soda K, Moriguchi M (January 1969). "Crystalline lysine decarboxylase". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 34 (1): 34–9. Bibcode:1969BBRC...34...34S. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(69)90524-5. PMID 5762458.
External links
- lysine+decarboxylase at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)