Malotilate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.056.334 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
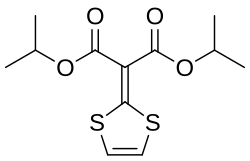
| Formula | C12H16O4S2 |
| Molar mass | 288.38 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Malotilate (INN) is a drug that has been used in studies for the treatment of liver disease. It has been shown to facilitate liver regeneration in rats.[1]
References
- ^ Niwano Y, Katoh M, Uchida M, Sugimoto T (1986). "Acceleration of Liver Regeneration by Malotilate in Partially Hepatectomized Rats". Japanese Journal of Pharmacology. 40 (3): 411–415. doi:10.1254/jjp.40.411. PMID 2423727.
- Bührer M, Le Cotonnec JY, Wermeille M, Bircher J (1986). "Treatment of liver disease with malotilate. A pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic phase II study in cirrhosis". Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 30 (4): 407–16. doi:10.1007/BF00607952. PMID 3743616. S2CID 19898827.
- Siegers CP, Pauli V, Korb G, Younes M (August 1986). "Hepatoprotection by malotilate against carbon tetrachloride-alcohol-induced liver fibrosis". Agents Actions. 18 (5–6): 600–3. doi:10.1007/BF01964970. PMID 3766314. S2CID 3213262.
- Younes M, Siegers CP (May 1985). "Effect of malotilate on paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity". Toxicol. Lett. 25 (2): 143–6. doi:10.1016/0378-4274(85)90074-8. PMID 4002245.