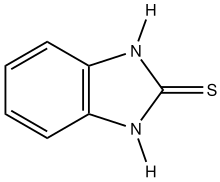
Mercaptobenzimidazole
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3-Dihydro-2H-1,3-benzimidazole-2-thione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.640 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2811 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H6N2S | |
| Molar mass | 150.20 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.42 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 298 °C (568 °F; 571 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Warning | |
| H302, H332, H361, H373, H410 | |
| P201, P202, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P281, P301+P312, P304+P312, P304+P340, P308+P313, P312, P314, P330, P391, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Mercaptobenzimidazole is the organosulfur compound with the formula C6H4(NH)2C=S. It is the mercaptan of benzimidazole. It is a white solid that has been investigated as a corrosion inhibitor. The name is a misnomer because the compound is a thiourea, characterized with a short C=S bond length of 169 pm.[1] A similar situation applies to 2-mercaptoimidazole, which is also a thiourea properly called 2-imidazolidinethione and mercaptobenzothiazole, which is also a thioamide.
It is prepared from o-phenylenediamine.[2]
References
- ^ Form, G. R.; Raper, E. S.; Downie, T. C. (1976). "The crystal and molecular structure of 2-mercaptobenzimidazole". Acta Crystallographica Section B: Structural Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry. 32 (2): 345–348. doi:10.1107/S0567740876003026.
- ^ VanAllan, J. A.; Deacon, B. D. (1950). "2-Mercaptobenzimidazole". Organic Syntheses. 30: 56. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.030.0056.