Myrtenal
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
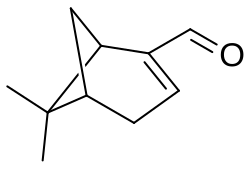
6,6-dimethylbicyclo[3.1.1]hept-2-ene-2-carbaldehyde
| |
| Other names
(1R)-2-Pinen-10-a
Benihinal | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.432 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | myrtenal |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14O | |
| Molar mass | 150.221 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.987 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 220-221 °C |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H227 | |
| P210, P280, P370+P378, P403+P235, P501 | |
| Flash point | 78 °C |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Myrtenal is a bicyclic monoterpenoid with the chemical formula C10H14O. It is a naturally occurring molecule that can be found in numerous plant species including Hyssopus officinalis, Salvia absconditiflora, and Cyperus articulatus.[1]
Biological research
Myrtenal was shown to inhibit acetylcholinesterase, which is a common method of treatment of alzheimer's disease and dementia, in-vitro.[2] In addition, mytenal has been shown to have antioxidant properties in rats.[3]
See also
References
- ^ "LOTUS: Natural Products Online". lotus.naturalproducts.net. Retrieved 2022-08-17.
- ^ Kaufmann D, Dogra AK, Wink M (October 2011). "Myrtenal inhibits acetylcholinesterase, a known Alzheimer target". The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 63 (10): 1368–1371. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.2011.01344.x. PMID 21899553. S2CID 44962827.
- ^ Lokeshkumar B, Sathishkumar V, Nandakumar N, Rengarajan T, Madankumar A, Balasubramanian MP (September 2015). "Anti-Oxidative Effect of Myrtenal in Prevention and Treatment of Colon Cancer Induced by 1, 2-Dimethyl Hydrazine (DMH) in Experimental Animals". Biomolecules & Therapeutics. 23 (5): 471–478. doi:10.4062/biomolther.2015.039. PMC 4556208. PMID 26336588.