Narirutin
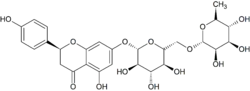 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S)-4′,5-Dihydroxy-7-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranosyloxy]flavan-4-one
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(22S,42S,43R,44S,45S,46R,72R,73R,74R,75R,76S)-14,25,43,44,45,73,74,75-Octahydroxy-76-methyl-22,23-dihydro-24H-3,6-dioxa-2(2,7)-[1]benzopyrana-4(2,6),7(2)-bis(oxana)-1(1)-benzenaheptaphan-24-one | |
| Other names
Naringenin-7-O-rutinoside
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.655 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H32O14 | |
| Molar mass | 580.539 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Narirutin is a flavanone-7-O-glycoside, consisting of the flavanone naringenin bonded with the disaccharide rutinose.[1]
It is found in orange juice.[1][2]
References
- ^ a b Rouseff, Russell L.; Martin, Shirley F.; Youtsey, Charles O. (1987). "Quantitative survey of narirutin, naringin, hesperidin, and neohesperidin in citrus". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 35 (6): 1027–1030. doi:10.1021/jf00078a040. ISSN 0021-8561.
- ^ Widmer W.W and Martin S.F. (1993). "Interferences with naringin and neohesperidin analysis by high performance liquid chromatography".
External links
 Media related to Narirutin at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Narirutin at Wikimedia Commons