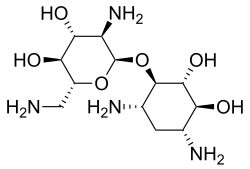
Neamine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Neomycin A |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H26N4O6 |
| Molar mass | 322.362 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Neamine (neomycin A) is a degradation product of the aminoglycoside antibiotic neomycin.[1] Several derivatives of neamine are active against susceptible and resistant Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.[2]
References
- ^ Leach BE, Teeters CM (June 1951). "Neamine, an Antibacterial Degradation Product of Neomycin". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 73 (6): 2794–2797. doi:10.1021/ja01150a107.
- ^ Zimmermann L, Bussière A, Ouberai M, Baussanne I, Jolivalt C, Mingeot-Leclercq MP, et al. (October 2013). "Tuning the antibacterial activity of amphiphilic neamine derivatives and comparison to paromamine homologues". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 56 (19): 7691–7705. doi:10.1021/jm401148j. PMID 24083676.