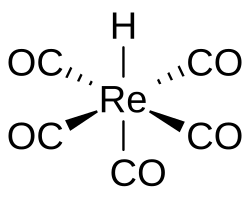
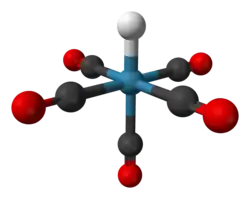
Pentacarbonylhydridorhenium
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
pentacarbonylhydridorhenium
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| ReH(CO)5 | |
| Molar mass | 327.265 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 2.30 g/mL, liquid |
| Melting point | 12.5 °C (54.5 °F; 285.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 100 °C (212 °F; 373 K) (decomposes) |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Flammable |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Pentacarbonylhydridorhenium is a chemical compound with the formula ReH(CO)5. This colorless liquid is a weak acid and represents one of the most important derivatives of dirhenium decacarbonyl (Re2(CO)10). It is synthesized by treating a methanolic solution of bromopentacarbonylrhenium(I) (Re(CO)5Br) with zinc and acetic acid (HOAc).[1]
- Re(CO)5Br + Zn + HOAc → ReH(CO)5 + ZnBrOAc
It is moderately sensitive to light: samples turn yellow due to the formation of the metal cluster Re3H(CO)14
- 3 Re(CO)5H → Re3H(CO)14 + H2 + CO
At 100 °C, it decomposes to Re2(CO)10:[1]
- 2 Re(CO)5H → H2 + Re2(CO)10
References
- ^ a b Michael A. Urbancic, John R. Shapley (1990). "Pentacarbonylhydridorhenium". Inorganic Syntheses. Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 28. pp. 165–8. doi:10.1002/9780470132593.ch43. ISBN 9780470132593.