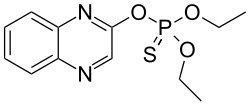
Quinalphos
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
O,O-Diethyl O-(quinoxalin-2-yl) phosphorothioate | |
| Other names
O,O-diethyl O-quinoxalin-2-yl phosphorothioate; Diethquinalphion; Diethquinalphione
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.033.650 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H15N2O3PS | |
| Molar mass | 298.30 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Reddish-brown liquid |
| Melting point | 31 °C (88 °F; 304 K) |
| 17.8 mg/L at 22 °C | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Quinalphos is an organothiophosphate chemical chiefly used as a pesticide. It is a reddish-brown liquid. The chemical formula is C12H15N2O3PS, and IUPAC name O,O-diethyl O-quinoxalin-2-yl phosphorothioate.[1] Ranked 'moderately hazardous' in World Health Organization's (WHO) acute hazard ranking, use of quinalphos, classified as a yellow label (highly toxic) pesticide in India, is widely used in the following crops: wheat, rice, coffee, sugarcane, and cotton.
References
- ^ "Central Insecticides Board & Registration Committee. 'List of Insecticides'". Archived from the original on 2012-01-09. Retrieved 2012-01-12.
External links
- Quinalphos in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)