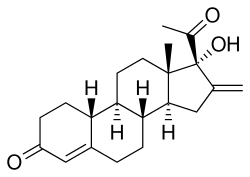
Segesterone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 17α-Hydroxy-16-methylene-19-norprogesterone; 16-Methylene-17α-hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-ene-3,20-dione; 17α-Deacetylnestorone |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H28O3 |
| Molar mass | 328.452 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Segesterone (INN, USAN),[1][2] also known as 17α-hydroxy-16-methylene-19-norprogesterone or as 17α-deacetylnestorone, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-norprogesterone group that was never marketed.[3] An acetate ester, segesterone acetate, better known as nestorone or elcometrine, is marketed for clinical use.[4] Segesterone acetate produces segesterone as a metabolite.[5]
References
- ^ International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN) (PDF). Vol. 17. World Health Organization. 2003. p. 210. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2022-01-20.
- ^ "7690-08-6 - SFLXYFZGKSGFKA-XUDSTZEESA-N - Segesterone [USAN:INN] - Similar structures search, synonyms, formulas, resource links, and other chemical information". ChemIDplus. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2016-08-11. Retrieved 2016-06-17.
- ^ "Segesterone". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Zavod RM (24 January 2012). "Chapter 41: Women's Health". In Lemke TL, Williams DA (eds.). Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 1403–. ISBN 978-1-60913-345-0.
- ^ Prasad PV, Bashir M, Sitruk-Ware R, Kumar N (March 2010). "Single-dose pharmacokinetics of Nestorone, a potential female-contraceptive". Steroids. 75 (3): 252–264. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2009.12.011. PMID 20064539. S2CID 205253216.