Selenium tetrabromide
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Tetrabromo-λ4-selane
| |
| Other names
Selenium tetrabromide, selenium(IV) bromide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.256 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| SeBr4 | |
| Molar mass | 398.576 |
| Density | 4.029 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 75 °C (167 °F; 348 K) (dissolves) |
| Boiling point | 115 °C (239 °F; 388 K) (sublimes) |
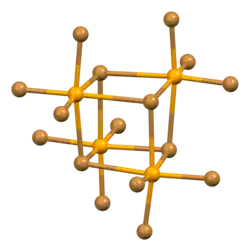
| Structure[1] | |
| trigonal (α) monoclinic (β) | |
| P31c, No. 159 (α) C2/c, No.15 (β) | |
Formula units (Z)
|
16 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| |
| Danger | |
| H301, H311, H314, H331, H351, H373, H410 | |
| P201, P202, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P281, P301+P310, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P310, P311, P312, P314, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Selenium tetrafluoride Selenium tetrachloride |
Other cations
|
Tellurium tetrabromide |
Related compounds
|
Selenium dibromide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Selenium tetrabromide is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula SeBr4.
Preparation
Selenium tetrabromide could be produced by mixing elemental bromine and selenium:[2][3]
Properties
Selenium tetrabromide exists in two polymorphs, the trigonal, black α-SeBr4 and the monoclinic, orange-reddish β-SeBr4, both of which feature tetrameric cubane-like Se4Br16 units but differ in how they are arranged.[1] It dissolves in carbon disulfide, chloroform and ethyl bromide, but decomposes in water,[4] so that it produces selenous acid in wet air.
The compound is only stable under a bromine-saturated atmosphere; gas phase measurements of the gas density indicate that the compound decomposes into selenium monobromide and bromine.[3]
References
- ^ a b Born, Ref. P.; Kniep, R.; Mootz, D. (1979). "Phasenbeziehungen im System Se-Br und die Kristallstrukturen des dimorphen SeBr4". Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 451 (1): 12–24. doi:10.1002/zaac.19794510103.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. pp. 772–774. doi:10.1016/C2009-0-30414-6. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ a b Tideswell, N. W.; McCullough, J. D. (1956). "Selenium Bromides. I. A Spectrophotometric Study of the Dissociation of Selenium Tetrabromide and Selenium Dibromide in Carbon Tetrachloride Solution1,2". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 78 (13): 3026–3029. doi:10.1021/ja01594a025.
- ^ Perry, Dale L. (2011). Handbook of Inorganic Compounds. CRC Press. p. 360. ISBN 978-1-4398-1461-1.