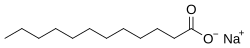
Sodium laurate
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Sodium dodecanoate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.076 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H23NaO2 | |
| Molar mass | 222.304 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.102 g/ml[1] |
| Melting point | 244 to 246 °C (471 to 475 °F; 517 to 519 K)[2] |
| Hazards | |
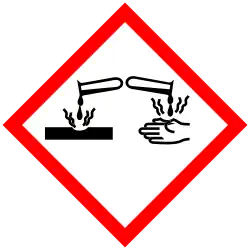
| GHS labelling: | |
| |
| Danger | |
| H315, H318, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Sodium laurate is a chemical compound with formula CH3(CH2)10CO2Na. As the sodium salt of a fatty acid (lauric acid), it is classified as a soap. It is a white solid.
Use
Sodium laurate is frequently used in bars of soap as an ingredient. Sodium laurate is also a permitted bleaching, washing and peeling agent.
Sodium Laurate has also been used to induce peripheral arterial disease in rats.[3]
References
- ^ Pathak, K. D.; Journal of the Indian Chemical Society 1953, V30, P47-51
- ^ Zacharie, Boulos; Organic Process Research & Development 2009, V13(3), P581-583
- ^ Wang Z (2018-01-10). "Low molecular weight fucoidan ameliorates hindlimb ischemic injury in type 2 diabetic rats". Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 210: 434–442. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2017.09.014. PMID 28917976. S2CID 2299321.