Sodium p-toluenesulfonate
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.476 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H7NaO3S | |
| Molar mass | 194.18 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Hazards | |
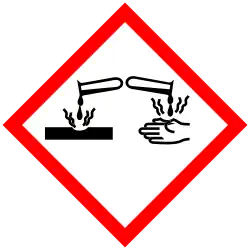
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
| |
| Danger | |
| H315, H318, H319 | |
| P264, P264+P265, P280, P302+P352, P305+P351+P338, P305+P354+P338, P317, P321, P332+P317, P337+P317, P362+P364 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Sodium p-toluenesulfonate is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4SO3Na. It is white, water-soluble solid. It is produced by the neutralization toluenesulfonic acid with sodium hydroxide. It is also a common product from the reactions of sodium-based reagents with toluenesulfonates.[1]
Heating this salt in strong base results in desulfonation, giving, after acid workup, p-cresol.[2]
References
- ^ Marc Julia, Michel Maumy (1976). "Free-Radical Cyclization: Ethyl 1-Cyano-2-Methylcyclohexanecarboxylate". Organic Syntheses. 55: 57. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.055.0057.
- ^ W. W. Hartman (1923). "p-Cresol". Organic Syntheses. 3: 37. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.003.0037.