Strontium lactate
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.045.363 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Sr(C3H5O3)2 | |
| Molar mass | 265.76 |
| Appearance | white powder[1] |
| Density | 1.276 g/cm3[2] |
| Boiling point | 227 °C (441 °F; 500 K)[2] |
| Soluble | |
| Hazards[2] | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H302, H312, H315, H319, H332, H335 | |
| P261, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P332+P313 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 109 °C (228 °F; 382 K)[2] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
900 mg/kg (Rat, intraperitoneal)[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
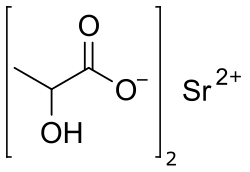
Strontium lactate is a chemical compound, a salt of strontium and lactic acid with the formula Sr(C3H5O3)2.[3][4]
Synthesis
Strontium lactate can be obtained by neutralizing moderately dilute lactic acid with strontium carbonate or hydroxide and evaporating the resulting solution to dryness with a moderate heat.[5]
References
- ^ "Strontium Lactate - 29870-99-3". Discovery Fine Chemicals. Retrieved 6 February 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f "Strontium lactate SDS" (PDF). www.pfaltzandbauer.com. Waterbury, CT, USA: Pfaltz & Bauer. Retrieved 20 August 2025.
- ^ "Strontium lactate". National Institute of Standards and Technology. 17 October 2019. Retrieved 6 February 2023.
- ^ "NCATS Inxight Drugs — STRONTIUM LACTATE". drugs.ncats.io. Retrieved 6 February 2023.
- ^ Caspari, Charles (1895). A Treatise on pharmacy for students and pharmacists. Lea. p. 477. Retrieved 6 February 2023.
