Sulfometuron methyl
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
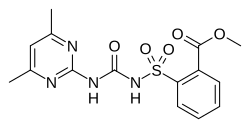
Methyl 2-{[(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)carbamoyl]sulfamoyl}benzoate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.070.688 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H16N4O5S | |
| Molar mass | 364.38 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 1.48 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 202 °C (396 °F; 475 K) |
| 244 mg/L | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 5.2 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
 
| |
| Warning | |
| H319, H332, H410 | |
| P261, P264+P265, P271, P273, P280, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P317, P337+P317, P391, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Sulfometuron methyl is an organic compound used as an herbicide.[1] It is classed as a sulfonylurea. It functions via the inhibition of the enzyme acetolactate synthase, which catalyzes the first step in biosynthesis of the branched-chain amino acids valine, leucine, and isoleucine.[2]
Sulfometuron methyl's HRAC classification is Group B (global, Aus), Group 2 (numeric), as it inhibits acetohydroxyacid synthase.[3]
References
- ^ "Sulfometuron-methyl". Extension Toxicology Network. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
- ^ LaRossa, Robert; Schloss, John (1984). "The Sulfonylurea Herbicide Sulfometuron Methyl Is an Extremely Potent and Selective Inhibitor of Acetolactate Synthase in Salmonella typhimurium". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 259 (14): 8753–8757. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)47217-6. PMID 6378902.
- ^ "Classification of Herbicides According to Site of Action". Retrieved 19 July 2025.