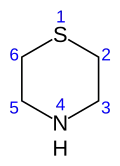
Thiomorpholine
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Thiomorpholine[1] | |||
| Other names
Thiamorpholine
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.238 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H9NS | |||
| Molar mass | 103.18 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Odor | Strong odor resembling piperidine[2] | ||
| Density | 1.0882 g/cm3 | ||
| Boiling point | 169 °C (336 °F; 442 K)[2] | ||
| Miscible[2] | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |||
Thiomorpholine, HN(CH2)4S, is a heterocyclic compound containing nitrogen and sulfur. It can be considered a thio analog of morpholine.
It can be prepared from cysteamine and vinyl chloride:[3]
- H2NCH2CH2SH + CH2=CHCl → HN(CH2)4S + HCl
References
- ^ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 142. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b c Merck Index, 12th Edition, monograph 9435, p. 1587
- ^ Steiner, Alexander; Nelson, Ryan C.; Dallinger, Doris; Kappe, C. Oliver (2022). "Synthesis of Thiomorpholine via a Telescoped Photochemical Thiol–Ene/Cyclization Sequence in Continuous Flow". Organic Process Research & Development. 26 (8): 2532–2539. doi:10.1021/acs.oprd.2c00214. PMC 9396661. PMID 36032361.