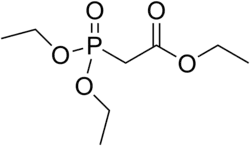
Triethyl phosphonoacetate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethyl (diethoxyphosphoryl)acetate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.598 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H17O5P | |
| Molar mass | 224.19 g/mol |
| Boiling point | 142 to 145 °C (288 to 293 °F; 415 to 418 K) at 9 mmHg |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Triethyl phosphonoacetate is a reagent for organic synthesis used in the Horner-Wadsworth-Emmons reaction (HWE) or the Horner-Emmons modification.
Triethyl phosphonoacetate can be added dropwise to sodium methoxide solution to prepare a phosphonate anion. It has an acidic proton that can easily be abstracted by a weak base. When used in an HWE reaction with a carbonyl the resulting alkene formed is usually the E alkene, and is generated with excellent regioselectivity.[1]
References
- ^ Rathke, Michael W.; Nowak, Michael (July 1985). "The Horner-Wadsworth-Emmons modification of the Wittig reaction using triethylamine and lithium or magnesium salts". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 50 (15): 2624–2626. doi:10.1021/jo00215a004.