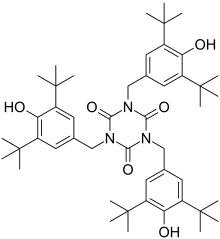
Tris(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzyl) isocyanurate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3,5-tris(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzyl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione | |
| Other names
Chemical names
Trade names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.044.165 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C48H69N3O6 | |
| Molar mass | 784.095 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 1.15 |
| Melting point | 219.4 °C (426.9 °F; 492.5 K) |
| <0.04 mg/l at 20°C | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Tris(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzyl) isocyanurate is a chemical compound used as a polymer stabilizer in plastics. Like other hindered phenols it acts as a primary antioxidant. More than 1000 tonnes per year are used in the EU.
Synthesis
It is formed by the Mannich reaction of 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol, cyanuric acid, and formaldehyde.
Properties and applications
Tris(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzyl) isocyanurate is a high molecular weight additive, with low volatility. It is well suited to stabilising polyolefins against degradation caused by long term heat aging.[1] It is an approved food contact material in the US.[2]
See also
- 1,3,5-Tris(4-(tert-butyl)-3-hydroxy-2,6-dimethylbenzyl)-1,3,5-triazinane-2,4,6-trione - related phenolic antioxidant with a cyanurate core
- Pentaerythritol tetrakis(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyhydrocinnamate) - a commonly used phenolic polymer stabiliser
References
- ^ Gijsman, Pieter; Fiorio, Rudinei (February 2023). "Long term thermo-oxidative degradation and stabilization of polypropylene (PP) and the implications for its recyclability". Polymer Degradation and Stability. 208: 110260. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2023.110260.
- ^ "Inventory of Food Contact Substances Listed in 21 CFR". www.hfpappexternal.fda.gov. Retrieved 4 December 2024.