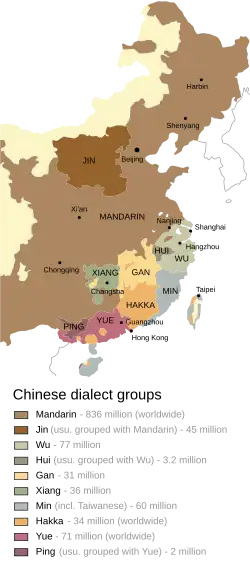
Wu–Hua Yue
| Wu-Hua Yue | |
|---|---|
| Ngfaa Yut | |
| Native to | People's Republic of China |
| Region | Guangxi |
| Speakers | 1.28 million (2012)[1] |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | None (mis) |
| ISO 639-6 | whua |
| Glottolog | wuhu1235 Wuhua |
| Linguasphere | 79-AAA-md |
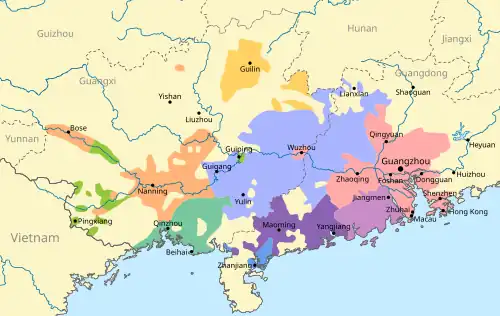 Wu-Hua (bottom), among other Yue and Pinghua groups in Guangxi and Guangdong. | |
Wu–Hua (Ng-faa, 吳化方言) is a branch of Yue Chinese spoken in Guangdong province composed of two dialects:
- Wuchuan dialect
- Huazhou dialect
References
- Li, Rong (2012), 中國語言地圖集 [Language Atlas of China] (in Chinese) (2 ed.), The Commercial Press, ISBN 978-7-100-07054-6.
Sino-Tibetan branches | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Western Himalayas (Himachal, Uttarakhand, Nepal, Sikkim) |
| 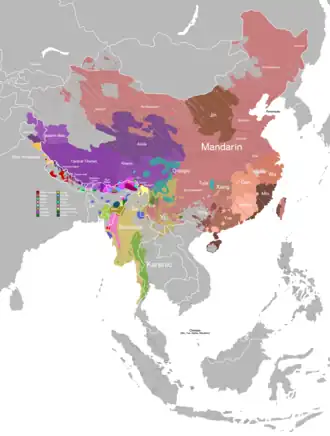 | |||
| Eastern Himalayas (Tibet, Bhutan, Arunachal) | |||||
| Myanmar and Indo- Burmese border |
| ||||
| East and Southeast Asia |
| ||||
| Dubious (possible isolates, Arunachal) |
| ||||
| Proposed groupings | |||||
| Proto-languages | |||||
Italics indicates single languages that are also considered to be separate branches. | |||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Additional terms may apply for the media files.