Atelerix
| Atelerix[1] | |
|---|---|

| |
| A. albiventris | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Eulipotyphla |
| Family: | Erinaceidae |
| Subfamily: | Erinaceinae |
| Genus: | Pomel, 1848 |
| Type species | |
| Erinaceus albiventris Wagner, 1841
| |
| Species | |
Atelerix is a genus of hedgehog in the family Erinaceidae. It contains four species, all native to Africa.[1]
Species
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Four-toed hedgehog
|
Atelerix albiventris (Wagner, 1841) |
Gambia and Senegal in the west, to Somalia in the east, and also in eastern Africa, as far south as Mozambique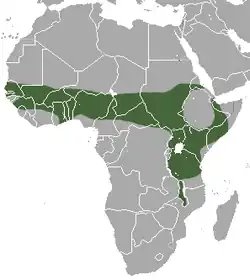
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| North African hedgehog
|
Atelerix algirus Lereboullet, 1842 |
Algeria, Libya, Malta, Morocco, Spain, and Tunisia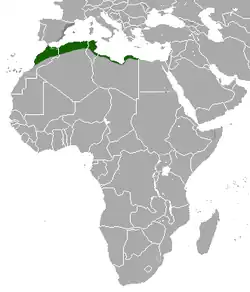
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| Southern African hedgehog
|
Atelerix frontalis (A. Smith, 1831) |
Angola, Botswana, Lesotho, Namibia, South Africa, Tanzania and Zimbabwe.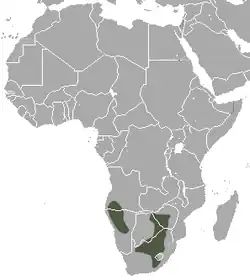
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| Somali hedgehog
|
Atelerix sclateri Anderson, 1895 |
Somalia.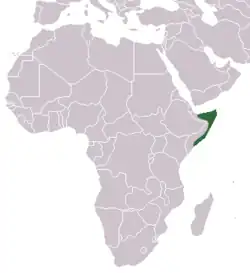
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
The Atelerix diversified from its family because of geographical isolation during Pleistocene climate changes. This being a type of vicariance separation from the Niger River. This allowed the Erinaceidane family to be more diverse.
References
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Atelerix.
- ^ a b Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M., eds. (2005). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.

.jpg)
