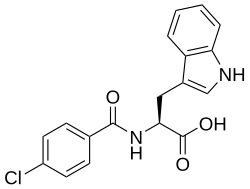
Benzotript
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Benzotrypt; CR-501; N-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-L-tryptophan; N-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-L-tryptophan; N-[(4-Chlorophenyl)carbonyl]tryptophan |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.049.528 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H15ClN2O3 |
| Molar mass | 342.78 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Benzotript (INN), also known as N-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-L-tryptophan, is a muscle relaxant that inhibits gastric secretion and was never marketed.[1][2] It is a tryptamine derivative and the N-(4-chlorobenzoyl) analogue of the amino acid tryptophan.[1] Similarly to proglumide (N2-benzoyl-N,N-dipropyl-α-glutamine), the drug acts as a competitive and non-selective cholecystokinin receptor antagonist.[2][3] Other more potent tryptophan derivatives have also been developed as cholecystokinin (CCK) antagonists.[2]
References
- ^ a b Elks J (2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer US. p. 1262. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3. Retrieved 8 October 2024.
- ^ a b c Herranz R (September 2003). "Cholecystokinin antagonists: pharmacological and therapeutic potential". Med Res Rev. 23 (5): 559–605. doi:10.1002/med.10042. PMID 12789687.
- ^ Maton PN, Jensen RT, Gardner JD (January 1986). "Cholecystokinin antagonists". Horm Metab Res. 18 (1): 2–9. doi:10.1055/s-2007-1012212. PMID 2419234.