Chlorquinaldol
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
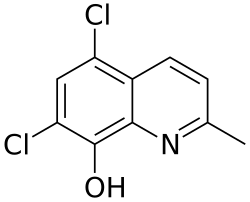
| Preferred IUPAC name
5,7-Dichloro-2-methylquinolin-8-ol | |
| Other names
Anginazol; Lacoid, Nerisone
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.718 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H7Cl2NO | |
| Molar mass | 228.07 g/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| D08AH02 (WHO) G01AC03 (WHO), P01AA04 (WHO), R02AA11 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Chlorquinaldol is an antimicrobial agent and antiseptic.[1] It is a chlorinated derivative of the popular chelating agent 8-hydroxyquinoline. It is applied topically as a cream and internally as a losenge.[2]
It was marketed by Geigy as an intestinal antiseptic and amebicide with the trade name Siosteran.
References
- ^ Mett H, Gyr K, Zak O, Vosbeck K (July 1984). "Duodeno-pancreatic secretions enhance bactericidal activity of antimicrobial drugs". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 26 (1): 35–8. doi:10.1128/aac.26.1.35. PMC 179912. PMID 6236746.
- ^ Kutscher, Bernhard (2020). "Dermatologicals ( D ), 4. Antiseptics and Disinfectants ( D 08), Anti‐Acne Preparations ( D 10), and Other Dermatological Preparations ( D 11)". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. pp. 1–22. doi:10.1002/14356007.w08_w03. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2.