Dilazep
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Comelian Kowa |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C31H44N2O10 |
| Molar mass | 604.697 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Dilazep is a vasodilator that acts as an adenosine reuptake inhibitor.[1][2]
It is used for the treatment of cardiopathy and renal disorders.[3]
Synthesis
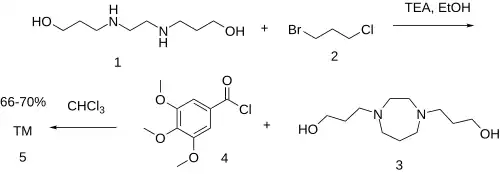
The reaction of bis(3-hydroxypropyl)ethylene diamine (1) with 1-bromo-3-chloropropane (2) gives the homopiperazine derivative 3. Esterification by reaction with 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl chloride (4) completes the synthesis of dilazep (5).[4][5][6]
See also
- Hexobendine, a drug with similar chemical structure
References
- ^ Deguchi H, Takeya H, Wada H, Gabazza EC, Hayashi N, Urano H, Suzuki K (September 1997). "Dilazep, an antiplatelet agent, inhibits tissue factor expression in endothelial cells and monocytes". Blood. 90 (6): 2345–56. doi:10.1182/blood.V90.6.2345. PMID 9310485.
- ^ PubChem. "Dilazep". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2021-08-18.
- ^ "Pharmaceuticals". Kowa Company Ltd.
- ^ Thieme
- ^ GB1107470 idem Herbert Arnold, Kurt Pahls, Rolf Rebling,Norbert Brock, Hans-Dieter Lenke, U.S. patent 3,532,685 (1970 to Asta Werke Ag Chem Fab)
- ^ Schlögl, K., Schlögl, R. (1964). "Über pharmakodynamisch wirksame 3,4,5-Trimethoxybenzoate und verwandte Ester von symmetrischen Bis-hydroxyalkylpiperazinen und-dialkylpolymethylendiaminen". Monatshefte für Chemie. 95 (3): 922–941. doi:10.1007/BF00908805.