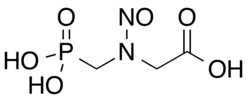
N-Nitrosoglyphosate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-Nitroso-N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
[Nitroso(phosphonomethyl)amino]acetic acid | |
| Other names
Nitrosoglyphosate, 56516-72-4, N-Nitrosoglyphosphate, 2-[nitroso(phosphonomethyl)amino]acetic acid, NNG
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H7N2O6P | |
| Molar mass | 198.071 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
N-Nitrosoglyphosate is the nitrosamine degradation product and synthetic impurity of glyphosate herbicide.
The US EPA limits N-nitrosoglyphosate impurity to a maximum of 1 ppm in glyphosate formulated products.[1] N-Nitrosoglyphosate can also form from the reaction of nitrates and glyphosate. Formation of N-nitrosoglyphosate has been observed in soils treated with sodium nitrite and glyphosate at elevated levels, though formation in soil is not expected at under typical field conditions.[2]
References
- ^ Pesticide Fact Sheet (Report). United States Environmental Protection Agency. June 1986. p. 4. Retrieved May 4, 2022.
- ^ Khan, Shahamat U. (December 9, 1981). "N-Nitrosamine Formation in Soil from the Herbicide Glyphosate and its Uptake by Plants". N-Nitroso Compounds. ACS Symposium Series. Vol. 174. AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY. pp. 275–287. doi:10.1021/bk-1981-0174.ch019. ISBN 0-8412-0667-8.