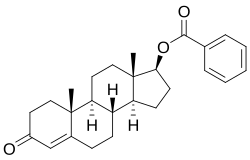
Testosterone benzoate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Testosterone 17β-benzoate; Androst-4-en-17β-ol-3-one 17β-benzoate |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.575 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H32O3 |
| Molar mass | 392.539 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Testosterone benzoate, or testosterone 17β-benzoate, also known as androst-4-en-17β-ol-3-one 17β-benzoate, is a synthetic, injected anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and an androgen ester – specifically, the benzoate C17β ester of testosterone – which was never marketed.[1][2] It is a prodrug of testosterone and, when administered via intramuscular injection, is associated with a long-lasting depot effect and extended duration of action.[3][4][5] The drug was first described in 1936 and was the first androgen ester and ester of testosterone to be synthesized.[6]
See also
References
- ^ Yalkowsky SH, He Y, Jain P (19 April 2016). Handbook of Aqueous Solubility Data, Second Edition. CRC Press. pp. 1313–. ISBN 978-1-4398-0246-5.
- ^ Archer T, Hansen S (5 September 2013). Behavioral Biology: Neuroendocrine Axis. Psychology Press. pp. 76–. ISBN 978-1-134-76125-8.
- ^ CIBA Foundation Symposium (17 September 2009). Hormones, Psychology and Behaviour, Volume 3: Book I of Colloquia on Endocrinology. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 260–. ISBN 978-0-470-71486-7.
- ^ Schaefer B (26 May 2015). Natural Products in the Chemical Industry. Springer. pp. 540–. ISBN 978-3-642-54461-3.
- ^ Lamparczyk H (21 August 1992). CRC Handbook of Chromatography: Analysis and Characterization of Steroids. CRC Press. pp. 34–. ISBN 978-0-8493-3008-7.
- ^ Parkes AS (1936). "Increasing the Effectiveness of Testosterone". The Lancet. 228 (5899): 674–676. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)80929-0. ISSN 0140-6736.