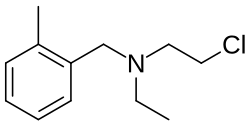
Xylamine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | N-2-Chloroethyl-N-ethyl-2-methylbenzylamine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H18ClN |
| Molar mass | 211.73 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Xylamine is a monoaminergic neurotoxin and benzylamine derivative that is closely related to DSP-4.[1][2] It is a relatively selective noradrenergic neurotoxin, which is attributed to its high affinity for the norepinephrine transporter (NET).[1] DSP-4 is generally preferred over xylamine for use in scientific research and hence xylamine is limitedly employed.[1] Xylamine was first described in 1975.[2][3]
References
- ^ a b c Kostrzewa RM (2022). "Survey of Selective Monoaminergic Neurotoxins Targeting Dopaminergic, Noradrenergic, and Serotoninergic Neurons". Handbook of Neurotoxicity. Cham: Springer International Publishing. pp. 159–198. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-15080-7_53. ISBN 978-3-031-15079-1.
- ^ a b Dudley MW, Howard BD, Cho AK (1990). "The interaction of the beta-haloethyl benzylamines, xylamine, and DSP-4 with catecholaminergic neurons". Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 30: 387–403. doi:10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.002131. PMID 2188573.
- ^ Krueger CA, Cook DA (November 1975). "Synthesis and adrenergic neuron blocking properties of some alkylating analogues of bretylium". Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 218 (1): 96–105. PMID 1212016.