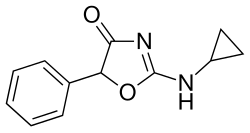
Cyclazodone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H12N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 216.240 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
| |
Cyclazodone is a centrally acting stimulant drug developed by American Cyanamid Company in the 1960s.[1] The drug is related to other drugs such as pemoline and thozalinone. It displayed a favorable therapeutic index and margin of safety in comparison to pemoline and other N-lower-alkyl-substituted pemoline derivatives.[2] The patents concluded that cyclazodone possessed properties efficacious in reducing fatigue and as a potential anorectic.[3] Structural congeners of pemoline have been described as "excitants with unique properties distinguishing them from the sympathomimetic amines" whilst displaying less stimulatory activity and toxicity compared to amphetamine.[4]
It is included under the World Anti-Doping Agency prohibited list.[5]
Safety
Cyclazodone has not been evaluated by the United States Food and Drug Administration for use in humans as a nootropic, anorectic, or stimulant and thus safety information is lacking. However, in studies relating to the therapeutic uses of cyclazodone, it was noted that it exhibited less cardiotoxic and hepatotoxic effects than D-amphetamine in studies on mice.[2]
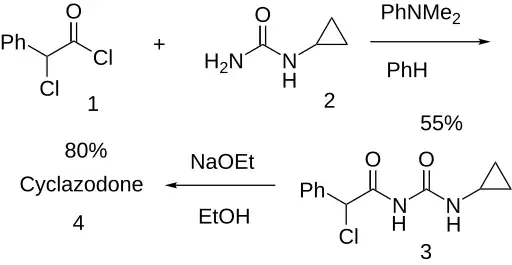
Synthesis
α-Chlorophenylacetyl chloride (1) and 1-cyclopropylurea (2) react to give the amide (3). The heterocycle cyclazodone is formed on threatment of this with sodium ethoxide.[2][6]
See also
References
- ^ US 3321470, Howell Jr CF, Hardy RA, Quinones N, "5-Arylidene-2-Amino-2-Oxazolin-4-Ones", issued 23 May 1967, assigned to American Cyanamid
- ^ a b c US 3609159, De Marne V, Pierre D, Guidicelli RL, Najer H, "5-Phenyl-2-Cyclopropylamino-4-Oxazolinone", issued 28 September 1971, assigned to Les Laboratoires Dausse
- ^ GB 1005738, De Marne V, Pierre D, Guidicelli RL, Najer H, "5-Phenyl-2-Cyclopropylamino-4-Oxazolinone", issued 29 September 1965, assigned to Les Laboratoires Dausse
- ^ Greenblatt EN, Osterberg AC (July 1965). "Some pharmacologic properties of thozalinone, a new excitant". Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 7 (4): 566–78. doi:10.1016/0041-008x(65)90042-6. PMID 4378772.
- ^ "World Anti-Doping Agency 2008 Prohibited List" (PDF). World Anti-Doping Agency. 22 September 2007.
- ^ Najer, H. et al, Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr., 1963, 1810.