Acetergamine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
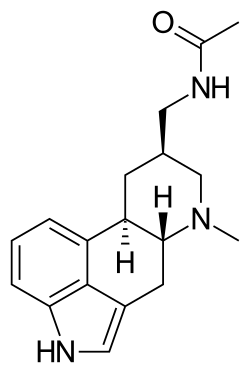
| Systematic IUPAC name
N-{[(8β)-6-Methylergolin-8-yl]methyl}acetamide | |
| Other names
8β-acetylaminomethyl-6-methylergoline
(+)-N-Acetyl-9,10-dihydrolysergamine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.281 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H23N3O | |
| Molar mass | 297.402 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Acetergamine is an organic chemical compound; specifically it is a derivative of ergoline, making it a member of the ergotamine family of compounds. Acetergamine currently has no mainstream uses, however its potential as an alpha-1 blocker and vasodilator has led to it being covered in several patents concerning therapies for erectile dysfunction. It has also been investigated as a treatment for cerebellar ataxia.[1]
References
| Ergolines (incl. lysergines) |
|
|---|---|
| Clavines (6,8-dimethylergolines) |
|
| Lysergamides (lysergic acid amides) |
|
| Ergopeptines (peptide ergolines) |
|
| Partial ergolines |
|
| Related compounds | |
| Natural sources |
|
| |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Additional terms may apply for the media files.